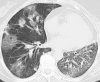
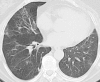
Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) after thoracic radiotherapy for breast carcinoma
- PMID: 17201913
- PMCID: PMC1780052
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-2-2
Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) after thoracic radiotherapy for breast carcinoma
Abstract
Common complications of thoracic radiotherapy include esophagitis and radiation pneumonitis. However, it is important to be aware of uncommon post-radiotherapy complications such as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP). We report on two patients with carcinoma of the breast who developed an interstitial lung disease consistent with BOOP. BOOP responds to treatment with corticosteroids and the prognosis is generally good despite of the need for long-term administration of corticosteroids as relapses can occur during tapering of steroids. This report provides guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of patients with pulmonary infiltrates after radiotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pulmonary damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1999 Apr 17;143(16):833-6. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1999. PMID: 10347650 Review. Dutch.
-
A survey of radiation-induced bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia syndrome after breast-conserving therapy in Japan.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008 May 1;71(1):123-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.09.003. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 18060702
-
A case of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia syndrome with preceding radiation pneumonitis after breast-conserving therapy.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004 Dec;34(12):755-8. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyh134. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15640508
-
Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia after tangential beam irradiation to the breast: discrimination from radiation pneumonitis.Radiat Med. 2002 May-Jun;20(3):151-4. Radiat Med. 2002. PMID: 12126090
-
[Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia after adjuvant thoracic radiotherapy for breast cancer: a case report].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Feb;39(2):122-5. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11321823 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Phase II study of high-dose [131I]metaiodobenzylguanidine therapy for patients with metastatic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Sep 1;27(25):4162-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.3496. Epub 2009 Jul 27. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19636009 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Steroid treatment increases the recurrence of radiation-induced organizing pneumonia after breast-conserving therapy.Cancer Med. 2014 Aug;3(4):947-53. doi: 10.1002/cam4.255. Epub 2014 May 3. Cancer Med. 2014. PMID: 24799363 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous resolution of thoracic radiation therapy-induced organizing pneumonia: A case series.Respir Med Case Rep. 2019 Jan 10;26:180-184. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.01.009. eCollection 2019. Respir Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30705815 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of COVID-19 Pneumonitis and ICI Induced Pneumonitis.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 29;10:577696. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.577696. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological targeting of BET proteins attenuates radiation-induced lung fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):998. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19343-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosiello RA MWW. Radiation-induced lung injury. Clin Chest Med. 1990;11:65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical