CYCLONET--an integrated database on cell cycle regulation and carcinogenesis
- PMID: 17202170
- PMCID: PMC1899094
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl912
CYCLONET--an integrated database on cell cycle regulation and carcinogenesis
Abstract
Computational modelling of mammalian cell cycle regulation is a challenging task, which requires comprehensive knowledge on many interrelated processes in the cell. We have developed a web-based integrated database on cell cycle regulation in mammals in normal and pathological states (Cyclonet database). It integrates data obtained by 'omics' sciences and chemoinformatics on the basis of systems biology approach. Cyclonet is a specialized resource, which enables researchers working in the field of anticancer drug discovery to analyze the wealth of currently available information in a systematic way. Cyclonet contains information on relevant genes and molecules; diagrams and models of cell cycle regulation and results of their simulation; microarray data on cell cycle and on various types of cancer, information on drug targets and their ligands, as well as extensive bibliography on modelling of cell cycle and cancer-related gene expression data. The Cyclonet database is also accessible through the BioUML workbench, which allows flexible querying, analyzing and editing the data by means of visual modelling. Cyclonet aims to predict promising anticancer targets and their agents by application of Prediction of Activity Spectra for Substances. The Cyclonet database is available at http://cyclonet.biouml.org.
Figures

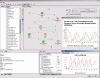
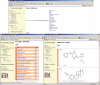

References
-
- Kolpakov F.A., Deineko I., Zhatchenko S.A., Kel A.E. Cyclonet—a database on cell cycle regulation. Proceedings of the 6th Russian Conference on Digital Libraries RCDL2004; September 29–October 1, 2004; Pushchino, Russia. 2004. pp. 4–9.
-
- Kolpakov F.A. BioUML—open source extensible workbench for systems biology. Proceedings of The Fourth International Conference on Bioinformatics of Genome Regulation and Structure; July 25–30, 2004; Novosibirsk, Russia. 2004. pp. 77–80.
-
- Kolpakov F., Puzanov M., Koshukov A. BioUML: visual modeling, automated code generation and simulation of biological systems. Proceedings of The Fifth International Conference on Bioinformatics of Genome Regulation and Structure; July 16–22, 2006; Novosibirsk, Russia. 2006. pp. 281–285.

