Protective effects of exercise and phosphoinositide 3-kinase(p110alpha) signaling in dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 17202264
- PMCID: PMC1766433
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0606663104
Protective effects of exercise and phosphoinositide 3-kinase(p110alpha) signaling in dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
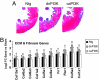
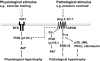
Physical activity protects against cardiovascular disease, and physiological cardiac hypertrophy associated with regular exercise is usually beneficial, in marked contrast to pathological hypertrophy associated with disease. The p110alpha isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) plays a critical role in the induction of exercise-induced hypertrophy. Whether it or other genes activated in the athlete's heart might have an impact on cardiac function and survival in a setting of heart failure is unknown. To examine whether progressive exercise training and PI3K(p110alpha) activity affect survival and/or cardiac function in two models of heart disease, we subjected a transgenic mouse model of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) to swim training, genetically crossed cardiac-specific transgenic mice with increased or decreased PI3K(p110alpha) activity to the DCM model, and subjected PI3K(p110alpha) transgenics to acute pressure overload (ascending aortic constriction). Life-span, cardiac function, and molecular markers of pathological hypertrophy were examined. Exercise training and increased cardiac PI3K(p110alpha) activity prolonged survival in the DCM model by 15-20%. In contrast, reduced PI3K(p110alpha) activity drastically shortened lifespan by approximately 50%. Increased PI3K(p110alpha) activity had a favorable effect on cardiac function and fibrosis in the pressure-overload model and attenuated pathological growth. PI3K(p110alpha) signaling negatively regulated G protein-coupled receptor stimulated extracellular responsive kinase and Akt (via PI3K, p110gamma) activation in isolated cardiomyocytes. These findings suggest that exercise and enhanced PI3K(p110alpha) activity delay or prevent progression of heart disease, and that supraphysiologic activity can be beneficial. Identification of genes important for hypertrophy in the athlete's heart could offer new strategies for treating heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
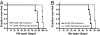

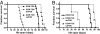
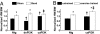

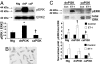
Similar articles
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase(p110alpha) plays a critical role for the induction of physiological, but not pathological, cardiac hypertrophy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 14;100(21):12355-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1934654100. Epub 2003 Sep 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14507992 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110α is a master regulator of exercise-induced cardioprotection and PI3K gene therapy rescues cardiac dysfunction.Circ Heart Fail. 2012 Jul 1;5(4):523-34. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.112.966622. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Circ Heart Fail. 2012. PMID: 22705768
-
Therapeutic targeting of oxidative stress with coenzyme Q10 counteracts exaggerated diabetic cardiomyopathy in a mouse model of diabetes with diminished PI3K(p110α) signaling.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Oct;87:137-47. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.028. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25937176
-
The IGF1-PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway in Mediating Exercise-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Protection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:187-210. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4304-8_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29098623 Review.
-
The protective effects of exercise and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (p110alpha) in the failing heart.Clin Sci (Lond). 2009 Mar;116(5):365-75. doi: 10.1042/CS20080183. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19175355 Review.
Cited by
-
Perturbations in the gene regulatory pathways controlling mitochondrial energy production in the failing heart.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1833(4):840-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22964268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Off-Target Effects of Cancer Therapy on Development of Therapy-Induced Arrhythmia: A Review.Cardiology. 2023;148(4):324-334. doi: 10.1159/000529260. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Cardiology. 2023. PMID: 36702116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Ischemic Effects of PIK3IP1 Are Mediated through Its Interactions with the ETA-PI3Kγ-AKT Axis.Cells. 2022 Jul 11;11(14):2162. doi: 10.3390/cells11142162. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883611 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxicity of kinase inhibitors: the prediction and translation of preclinical models to clinical outcomes.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Feb;10(2):111-26. doi: 10.1038/nrd3252. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21283106 Review.
-
MicroRNAs 29 are involved in the improvement of ventricular compliance promoted by aerobic exercise training in rats.Physiol Genomics. 2011 Jun 15;43(11):665-73. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00145.2010. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Physiol Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21447748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Briazgounov IP. World Health Stat Q. 1988;41:242–250. - PubMed
-
- Barker WH, Mullooly JP, Getchell W. Circulation. 2006;113:799–805. - PubMed
-
- Cohn JN, Bristow MR, Chien KR, Colucci WS, Frazier OH, Leinwand LA, Lorell BH, Moss AJ, Sonnenblick EH, Walsh RA, et al. Circulation. 1997;95:766–770. - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB, Castelli WP. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1561–1566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

