Characteristics of the m2000 automated sample preparation and multiplex real-time PCR system for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 17202273
- PMCID: PMC1829145
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01956-06
Characteristics of the m2000 automated sample preparation and multiplex real-time PCR system for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
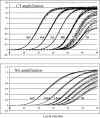
We evaluated a new real-time PCR-based prototype assay for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae developed by Abbott Molecular Inc. This assay is designed to be performed on an Abbott m2000 real-time instrument system, which consists of an m2000sp instrument for sample preparation and an m2000rt instrument for real-time PCR amplification and detection. The limit of detection of this prototype assay was determined to be 20 copies of target DNA for both C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae, using serially diluted linearized plasmids. No cross-reactivity could be detected when 55 nongonococcal Neisseria isolates and 3 non-C. trachomatis Chlamydia isolates were tested at 1 million genome equivalents per reaction. Concordance with the Roche Amplicor, BDProbeTec ET, and Gen-Probe APTIMA Combo 2 tests was assessed using unlinked/deidentified surplus clinical specimens previously analyzed with these tests. For C. trachomatis, concordance for positive results ranged from 93.7% to 100%, while concordance for negative results ranged from 98.2% to 100%. For N. gonorrhoeae, concordance for positive and negative results ranged from 91.4% to 100% and 99.3% to 100%, respectively. A workflow analysis of the prototype assay was conducted to obtain information on throughput under laboratory conditions. At 48 samples/run, the time to first result for both C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae was 4.5 h. A total of 135 patient specimens could be analyzed in 8.9 h, with 75 min of hands-on time. This study demonstrated the technical and clinical feasibility of the new Abbott real-time PCR C. trachomatis/N. gonorrhoeae assay.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison between the LCx Probe system and the COBAS AMPLICOR system for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections in patients attending a clinic for treatment of sexually transmitted diseases in Amsterdam, The Netherlands.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(3):829-35. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.829-835.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11230391 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of an automated extraction method for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by Cobas Amplicor PCR from different sample materials.Scand J Infect Dis. 2007;39(5):405-8. doi: 10.1080/00365540601087582. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17464862
-
Comparison of three in-house multiplex PCR assays for the detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis using real-time and conventional detection methodologies.Pathology. 2005 Oct;37(5):364-70. doi: 10.1080/00313020500254552. Pathology. 2005. PMID: 16194847
-
Molecular diagnostics. The polymerase chain reaction and its use in the diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Gac Med Mex. 1997;133 Suppl 1:133-7. Gac Med Mex. 1997. PMID: 9504115 Review.
-
Molecular genetic methods for diagnosis and characterisation of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: impact on epidemiological surveillance and interventions.APMIS. 2004 Nov-Dec;112(11-12):771-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2004.apm11211-1205.x. APMIS. 2004. PMID: 15638837 Review.
Cited by
-
[Diagnosis and treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis infections].Hautarzt. 2012 Jan;63(1):16-23. doi: 10.1007/s00105-011-2194-x. Hautarzt. 2012. PMID: 22146894 German.
-
Taqman real-time PCR detects Avipoxvirus DNA in blood of Hawai'i 'amakihi (Hemignathus virens).PLoS One. 2010 May 27;5(5):e10745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010745. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20523726 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of gonococcal and chlamydial infections among men who have sex with men in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 16;13(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02704-z. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39550563 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis today: treatment, detection, immunogenetics and the need for a greater global understanding of chlamydial disease pathogenesis.Drugs Today (Barc). 2009 Nov;45 Suppl B(Suppl B):25-31. Drugs Today (Barc). 2009. PMID: 20011691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Abbott m2000 RealTime human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) assay for HIV load monitoring in South Africa compared to the Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas Amplicor, Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas TaqMan HIV-1, and BioMerieux NucliSENS EasyQ HIV-1 assays.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Jul;47(7):2209-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01761-08. Epub 2009 May 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19420172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cates, W., and J. N. Wasserheit. 1991. Genital Chlamydia infections; epidemiology and reproductive sequelae. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 164:1771-1781. - PubMed
-
- Chernesky, M., D. Jang, K. Luinstra, S. Chong, M. Smieja, W. Cai, B. Hayhoe, E. Portillo, C. MacRitchie, C. Main, and R. Ewert. 2006. High analytical sensitivity and low rates of inhibition may contribute to detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in significantly more women by the APTIMA Combo 2 assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:400-405. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chong, S., D. Jang, X. Song, J. Mahony, A. Petrich, P. Barriga, and M. Chernesky. 2003. Specimen processing and concentration of Chlamydia trachomatis added can influence false-negative rates in the LCx assay but not in the APTIMA Combo 2 assay when testing for inhibitors. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:778-782. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

