Opposing actions of chronic Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinoid antagonists on hippocampal long-term potentiation
- PMID: 17202425
- PMCID: PMC1828281
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.439007
Opposing actions of chronic Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinoid antagonists on hippocampal long-term potentiation
Abstract
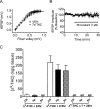
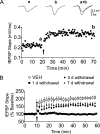
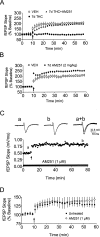
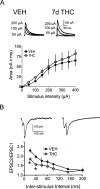
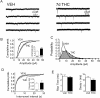
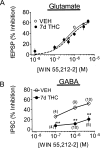
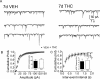
Memory deficits produced by marijuana arise partly via interaction of the psychoactive component, Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta(9)-THC), with cannabinoid receptors in the hippocampus. Although cannabinoids acutely reduce glutamate release and block hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP), a potential substrate for learning and memory, the consequences of prolonged exposure to Delta(9)-THC for hippocampal function are poorly understood. Rats were injected with Delta(9)-THC (10 mg/kg, i.p., q.d.) for 1, 3, or 7 d, and electrophysiological recordings were performed in hippocampal slices 1d after the final injection. At this time, Delta(9)-THC was undetectable in hippocampus using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Hippocampal LTP generated using high-frequency (HFS) or theta burst stimulation was not observed in brain slices from the 7-d Delta(9)-THC-treated animals. Delta(9)-THC also blocked HFS-LTP after 3 d, but not 1 d of treatment. The complete blockade of LTP persisted for 3 d after the last Delta(9)-THC injection, and full reversal of the LTP deficit was not observed up to 14 d following Delta(9)-THC withdrawal. The cannabinoid antagonist AM251 (2 mg/kg), administered before each Delta(9)-THC injection prevented the blockade of LTP, and 7-d treatment with AM251 alone significantly increased the level of LTP. Chronic Delta(9)-THC also produced tolerance to the inhibition of synaptic GABA, but not glutamate release by the agonist WIN55,212-2. These data define consequences of repeated Delta(9)-THC exposure for synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus that may help explain memory impairments in humans following chronic marijuana use.
Figures

References
-
- Bliss T.V., Collingridge G.L. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer R.D., Wong T., Nouranifar R., Iyengar R., Landau E.M. Postsynaptic CAMP pathway gates early LTP in hippocampal CA1 region. Neuron. 1995;15:1403–1414. - PubMed
-
- Bohme G.A., Laville M., Ledent C., Parmentier M., Imperato A. Enhanced long-term potentiation in mice lacking cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Neuroscience. 2000;95:5–7. - PubMed
-
- Bolla K.I., Brown K., Eldreth D., Tate K., Cadet J.L. Dose-related neurocognitive effects of marijuana use. Neurology. 2002;59:1337–1343. - PubMed
-
- Boyd S.T., Fremming B.A. Rimonabant—A selective CB1 antagonist. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005;39:684–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
