RalA and RalB function as the critical GTP sensors for GTP-dependent exocytosis
- PMID: 17202486
- PMCID: PMC6672288
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2537-06.2007
RalA and RalB function as the critical GTP sensors for GTP-dependent exocytosis
Abstract
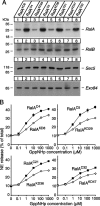
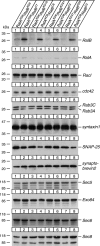
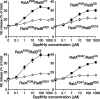
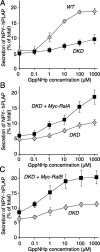
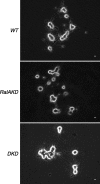
Although it has been established that the activation of GTPases by non-hydrolyzable GTP stimulates neurotransmitter release from many different secretory cell types, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In the present study we aimed to elucidate the functional role(s) for endogenous Ras-like protein A (RalA) and RalB GTPases in GTP-dependent exocytosis. For this purpose stable neuroendocrine pheochromocytoma 12 (PC12) cell lines were generated in which the expressions of both RalA and RalB were strongly downregulated. In these double knock-down cells GTP-dependent exocytosis was reduced severely and was restored after the expression of RalA or RalB was reintroduced by transfection. In contrast, Ca2+-dependent exocytosis and the docking of dense core vesicles analyzed by electron microscopy remained unchanged in the double knock-down cells. Furthermore, the transfected RalA and RalB appeared to be localized primarily on the dense core vesicles in undifferentiated and nerve growth factor-differentiated PC12 cells. Our results indicate that endogenous RalA and RalB function specifically as GTP sensors for the GTP-dependent exocytosis of dense core vesicles, but they are not required for the general secretory pathways, including tethering of vesicles to the plasma membrane and Ca2+-dependent exocytosis.
Figures





References
-
- Ahnert-Hilger G, Wegenhorst U, Stecher B, Spicher K, Rosenthal W, Gratz M. Exocytosis from permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells is differently modulated by guanosine 5′-[γ-thio]triphosphate and guanosine 5′-[βγ-imido]triphosphate. Evidence for the involvement of various guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochem J. 1992;284:321–326. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arac D, Chen X, Khant HA, Ubach J, Ludtke SJ, Kikkawa M, Johnson AE, Chiu W, Südhof TC, Rizo J. Close membrane–membrane proximity induced by Ca2+-dependent multivalent binding of synaptotagmin-1 to phospholipids. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A, Kowalchyk JA, DasGupta BR, Martin TF. SNAP-25 is required for a late postdocking step in Ca2+-dependent exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20227–20230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
