Nonredundant role of Akt2 for neuroprotection of rod photoreceptor cells from light-induced cell death
- PMID: 17202487
- PMCID: PMC6672299
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0445-06.2007
Nonredundant role of Akt2 for neuroprotection of rod photoreceptor cells from light-induced cell death
Abstract
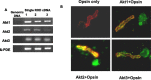
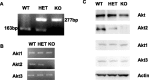
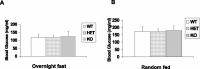
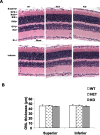
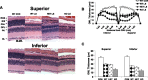
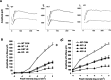
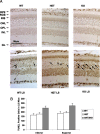
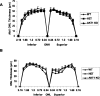
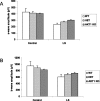
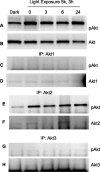
The Akt kinases mediate cell survival through phosphorylation and inactivation of apoptotic machinery components. Akt signaling provides a trophic signal for transformed retinal neurons in culture, but the in vivo role of Akt activity is unknown. In this study, we found that all three Akt isoforms were expressed in rod photoreceptor cells. We investigated the functional roles of Akt1 and Akt2, two of the isoforms of Akt, and their biological significance in light-induced retinal degeneration. Consistent with the hypothesis that Akt activity is important to circumvent stress-induced apoptosis, herein we report the novel finding that rod photoreceptor cells in Akt2 knock-out mice exhibited a significantly greater sensitivity to stress-induced cell death than rods in heterozygous or wild-type mice. Under similar conditions, Akt1 deletion had no effect on the retina. The presence of three Akt isoforms in the retina is suggestive of a functional redundancy; however, our studies clearly demonstrate that, under stress, Akt1 and Akt3 cannot complement the specific survival signals driven by Akt2. Furthermore, we show that Akt2 is specially activated is response to light stress. The results presented in this study provide the first direct evidence that Akt2 has a nonredundant neuroprotective role in photoreceptor survival and maintenance.
Figures

References
-
- Barber AJ, Nakamura M, Wolpert EB, Reiter CE, Seigel GM, Antonetti DA, Gardner TW. Insulin rescues retinal neurons from apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-mediated mechanism that reduces the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:32814–32821. - PubMed
-
- Bilton RL, Booker GW. The subtle side to hypoxia inducible factor (HIFalpha) regulation. Eur J Biochem. 2003;270:791–798. - PubMed
-
- Brazil DP, Hemmings BA. Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:657–664. - PubMed
-
- Brodbeck D, Cron P, Hemmings BA. A human protein kinase Bgamma with regulatory phosphorylation sites in the activation loop and in the C-terminal hydrophobic domain. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:9133–9136. - PubMed
-
- Brozinick JT, Jr, Roberts BR, Dohm GL. Defective signaling through Akt-2 and -3 but not Akt-1 in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle: potential role in insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2003;52:935–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- EY016507/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY00871/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY04149/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009769/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY1765/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY09769/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY004859/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY000871/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY016507/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY04859/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY001765/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY012190/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY12190/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR17703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY004149/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
