Cex1p is a novel cytoplasmic component of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear tRNA export machinery
- PMID: 17203074
- PMCID: PMC1783447
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601493
Cex1p is a novel cytoplasmic component of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear tRNA export machinery
Abstract
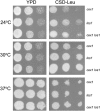
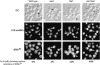
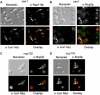
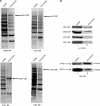
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yor112wp, which we named Cex1p, was identified using a yeast tRNA three-hybrid interaction approach and an in vivo nuclear tRNA export assay as a cytoplasmic component of the nuclear tRNA export machinery. Cex1p binds tRNA saturably, and associates with the nuclear pore complex by interacting directly with Nup116p. Cex1p co-purifies with the nuclear tRNA export receptors Los1p and Msn5p, the eukaryotic elongation factor eEF-1A, which delivers aminoacylated tRNAs to the ribosome, and the RanGTPase Gsp1p, but not with Cca1p, a tRNA maturation enzyme that facilitates translocation of non-aminoacylated tRNAs across the nuclear pore complex. Depletion of Cex1p and eEF-1A or Los1p significantly reduced the efficiency of nuclear tRNA export. Cex1p interacts with Los1p but not with eEF-1A in vitro. These findings suggest that Cex1p is a component of the nuclear aminoacylation-dependent tRNA export pathway in S. cerevisiae. They also suggest that Cex1p collects aminoacyl-tRNAs from the nuclear export receptors at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex, and transfers them to eEF-1A using a channelling mechanism.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cex1p facilitates Rna1p-mediated dissociation of the Los1p-tRNA-Gsp1p-GTP export complex.Traffic. 2012 Feb;13(2):234-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01304.x. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Traffic. 2012. PMID: 22008473
-
Utp22p acts in concert with Utp8p to channel aminoacyl-tRNA from the nucleolus to the nuclear tRNA export receptor Los1p but not Msn5p.Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Dec;90(6):731-49. doi: 10.1139/o2012-034. Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23194188
-
The nuclear tRNA aminoacylation-dependent pathway may be the principal route used to export tRNA from the nucleus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem J. 2004 Mar 15;378(Pt 3):809-16. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031306. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14640976 Free PMC article.
-
Review: transport of tRNA out of the nucleus-direct channeling to the ribosome?J Struct Biol. 2000 Apr;129(2-3):288-94. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.2000.4226. J Struct Biol. 2000. PMID: 10806079 Review.
-
A novel family of nuclear transport receptors mediates the export of messenger RNA to the cytoplasm.Eur J Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;81(11):577-84. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00273. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12498157 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytosolic Hsp70 and co-chaperones constitute a novel system for tRNA import into the nucleus.Elife. 2015 Apr 8;4:e04659. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04659. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25853343 Free PMC article.
-
Cex1 is a component of the COPI intracellular trafficking machinery.Biol Open. 2021 Mar 22;10(3):bio058528. doi: 10.1242/bio.058528. Biol Open. 2021. PMID: 33753324 Free PMC article.
-
Scyl1 facilitates nuclear tRNA export in mammalian cells by acting at the nuclear pore complex.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Jul 15;21(14):2483-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e10-03-0176. Epub 2010 May 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20505071 Free PMC article.
-
Utp9p facilitates Msn5p-mediated nuclear reexport of retrograded tRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Dec;20(23):5007-25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-06-0490. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19812255 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complexes: molecular multitasking revealed.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 Jul;32(4):705-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00119.x. Epub 2008 Jun 3. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18522650 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arts GJ, Fornerod M, Mattaj IW (1998a) Identification of a nuclear export receptor for tRNA. Curr Biol 8: 305–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

