Diagnosis and treatment of gallbladder perforation
- PMID: 17203529
- PMCID: PMC4087551
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i48.7832
Diagnosis and treatment of gallbladder perforation
Abstract
Aim: To present our clinical experience with gallbladder perforation cases.
Methods: Records of 332 patients who received medical and/or surgical treatment with the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis in our clinic between 1997 and 2006 were reviewed retrospectively. Sixteen (4.8%) of those patients had gallbladder perforation. The parameters including age, gender, time from the onset of symptoms to the time of surgery, diagnostic procedures, surgical treatment, morbidity, and mortality were evaluated.
Results: Seven patients had type I gallbladder perforation, 7 type II gallbladder perforation, and 2 type III gallbladder perforation according to Niemeier's classification. The patients underwent surgery after administration of intravenous electrolyte solutions, and were treated with analgesics and antibiotics within the first 36 h (mean 9 h) after admission. Two patients died of sepsis and multiple organ failure in the early postoperative period. Subhepatic abscess, pelvic abscess, pneumonia, pancreatitis, and acute renal failure were found in 6 patients.
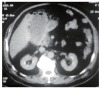
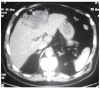
Conclusion: Early diagnosis and emergency surgical treatment of gallbladder perforation are of crucial importance. Upper abdominal computerized tomography for acute cholecystitis patients may contribute to the preoperative diagnosis of gallbladder perforation.
Figures
References
-
- Roslyn JJ, Thompson JE, Darvin H, DenBesten L. Risk factors for gallbladder perforation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987;82:636–640. - PubMed
-
- Sood BP, Kalra N, Gupta S, Sidhu R, Gulati M, Khandelwal N, Suri S. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of gallbladder perforation. J Clin Ultrasound. 2002;30:270–274. - PubMed
-
- Lennon F, Green WE. Perforation of the gallbladder. A review of 32 cases. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1983;28:169–173. - PubMed
-
- Lein HH, Huang CS. Male gender: risk factor for severe symptomatic cholelithiasis. World J Surg. 2002;26:598–601. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical