Maternal taurine supplementation in the late pregnant rat stimulates postnatal growth and induces obesity and insulin resistance in adult offspring
- PMID: 17204495
- PMCID: PMC2151367
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124610
Maternal taurine supplementation in the late pregnant rat stimulates postnatal growth and induces obesity and insulin resistance in adult offspring
Abstract
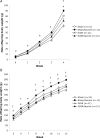
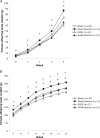
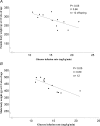
An adequate supply of taurine during fetal life is important for normal beta-cell development and insulin action. An altered availability of taurine may programme glucose metabolism in utero and result in type 2 diabetes in adult age. We examined whether maternal taurine supplementation in late pregnant rats affects postnatal growth, adult body composition, insulin sensitivity and endogenous insulin secretion in intrauterine growth restricted (IUGR) and normal offspring. Uterine artery ligation or sham operations were performed on gestational day (GD) 19. Taurine supplementation was given to half of the dams from GD 18 until term, resulting in four groups of offspring: sham (n = 22), sham/taurine (n = 22), IUGR (n = 22) and IUGR/taurine (n = 24). The offspring were studied at 12 weeks of age. In offspring with normal birth weight, fetal taurine supplementation markedly stimulated postnatal growth. In sham/taurine females, fat depots, plasma free fatty acid and leptin concentrations were increased, and insulin sensitivity was reduced. Insulin sensitivity was unaltered in IUGR and IUGR/taurine offspring. However, whereas IUGR offspring showed little catch-up growth, 50% of IUGR/taurine animals displayed complete catch-up at 12 weeks of age, and these animals had increased fat depots and reduced insulin sensitivity. In conclusion, taurine supplementation in late gestation resulted in accelerated postnatal growth, which was associated with adult obesity and insulin resistance in both IUGR and normal offspring. This effect was particularly evident in females. These data suggest that fetal taurine availability is an important determinant for postnatal growth, insulin sensitivity and fat accumulation.
Figures
References
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. Metabolic syndrome – a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med. 2006;23:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Anuradha CV, Balakrishnan SD. Taurine attenuates hypertension and improves insulin sensitivity in the fructose-fed rat, an animal model of insulin resistance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999;77:749–754. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Osmond C, Forsen TJ, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1802–1809. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein IGS. Obstetrics. Intrauterine Growth Restriction. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1996.
-
- Bosello O, Zamboni M. Visceral obesity and metabolic syndrome. Obesity Rev. 2000;1:47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

