Reversible inhibition of GABAA receptors by alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on the vertebrate postsynaptic neurons
- PMID: 17204496
- PMCID: PMC2151364
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124578
Reversible inhibition of GABAA receptors by alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on the vertebrate postsynaptic neurons
Abstract
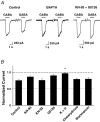
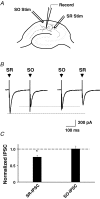
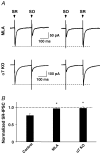
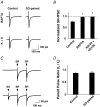
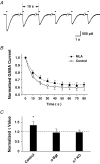
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are expressed throughout the central nervous system and influence a variety of higher order functions including learning and memory. While the effects of presynaptic nAChRs on transmitter release have been well documented, little is known about possible postsynaptic actions. A major species of neuronal nAChRs contains the alpha7 gene product and has a high relative permeability to calcium. Both on rodent hippocampal interneurons and on chick ciliary ganglion neurons these alpha7-nAChRs are often closely juxtaposed to GABAA receptors. We show here that in both cases activation of alpha7-nAChRs on the postsynaptic neuron acutely down-regulates GABA-induced currents. Nicotine application to dissociated ciliary ganglion neurons diminished subsequent GABAA receptor responses to GABA. The effect was blocked by alpha7-nAChR antagonists, by chelation of intracellular Ca2+ with BAPTA, and by inhibition of both Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and mitogen-activated protein kinase. A similar outcome was obtained in the hippocampus where electrical stimulation to activate cholinergic fibres reduced the amplitude of subsequent GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic currents. The reduction showed the same calcium and kinase dependence seen in ciliary ganglion neurons and was absent in hippocampal slices from alpha7-nAChR knockout mice. Moreover, alpha7-nAChR blockade in hippocampal slices reduced rundown of GABAA receptor-mediated whole-cell responses, indicating ongoing endogenous modulation. The results demonstrate regulation of GABAA receptors by alpha7-nAChRs on the postsynaptic neuron and identify a new mechanism by which nicotinic cholinergic signalling influences nervous system function.
Figures


References
-
- Adams CE, Broide RS, Chen Y, Winzer-Serhan UH, Henderson TA, Leslie FM, Freedman R. Development of the α7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor in rat hippocampal formation. Dev Brain Res. 2002;139:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EFR, Albuquerque EX. α-Bungarotoxin- and methyllycaconitine-sensitive nicotinic receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in interneurons of rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1998;810:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EFR, Barbosa CTF, Albuquerque EX. Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation modulates γ-aminobutyric acid release from CA1 neurons of rat hippocampal slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;283:1396–1411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

