GABA excitation in mouse hilar neuropeptide Y neurons
- PMID: 17204505
- PMCID: PMC2075399
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.019356
GABA excitation in mouse hilar neuropeptide Y neurons
Abstract
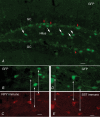
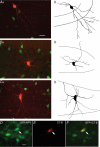
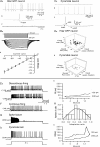
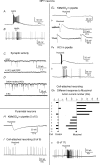
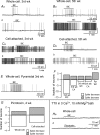
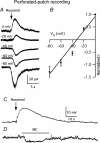
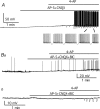
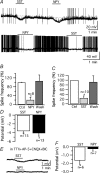
Neuropeptide Y-containing interneurons in the dentate hilar area play an important role in inhibiting the activity of hippocampal circuitry. Hilar cells are often among the first lost in hippocampal epilepsy. As many types of neurons are found in the hilus, we used a new transgenic mouse expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) in a subset of neurons that colocalized neuropeptide Y (NPY), somatostatin (SST), and GABA for whole-cell, perforated, and cell-attached recording in 240 neurons. As these neurons have not previously been identifiable in live slices, they have not been the focus of physiological analysis. Hilar NPY neurons showed modest spike frequency adaptation, a large 15.6 +/- 1.0 mV afterhyperpolarization, a mean input resistance of 335 +/- 26 M Omega, and were capable of fast-firing. Muscimol-mediated excitatory actions were found in a nominally Ca(2+)-free/high-Mg(2+) bath solution using cell-attached recording. GABA(A) receptor antagonists inhibited half the recorded neurons and blocked burst firing. Gramicidin perforated-patch recording revealed a GABA reversal potential positive to both the resting membrane potential and spike threshold. Together, these data suggest GABA is excitatory to many NPY cells. NPY and SST consistently hyperpolarized and reduced spike frequency in these neurons. No hyperpolarization of NPY on membrane potential was detected in the presence of tetrodotoxin, AP5, CNQX and bicuculline, supporting an indirect effect. Under similar conditions, SST hyperpolarized the cells, suggesting a direct postsynaptic action. Depolarizing actions of GABA and GABA-dependent burst-firing may synchronize a rapid release of GABA, NPY, and SST, leading to pre- and postsynaptic inhibition of excitatory hippocampal circuits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Excitatory and inhibitory synapses in neuropeptide Y-expressing striatal interneurons.J Neurophysiol. 2009 Nov;102(5):3038-45. doi: 10.1152/jn.00272.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 16. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19759327 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha5GABAA receptors regulate the intrinsic excitability of mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Oct;98(4):2244-54. doi: 10.1152/jn.00482.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 22. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17715197
-
A novel functionally distinct subtype of striatal neuropeptide Y interneuron.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 16;31(46):16757-69. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2628-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22090502 Free PMC article.
-
Interneurons in rat hippocampus after cerebral ischemia. Morphometric, functional, and therapeutic investigations.Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1993;150:1-32. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1993. PMID: 7907456 Review.
-
GABA-mediated synchronous potentials and seizure generation.Epilepsia. 1996 Nov;37(11):1035-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1996.tb01022.x. Epilepsia. 1996. PMID: 8917052 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy: can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection?Epilepsy Behav. 2014 Sep;38:117-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.12.001. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Epilepsy Behav. 2014. PMID: 24433836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous GAD65 Expression in Subtypes of GABAergic Neurons Across Layers of the Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Nov 3;15:750869. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.750869. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34803625 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the cAMP-dependent pathway in the reduction of epileptiform bursting caused by somatostatin in the mouse hippocampus.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;378(6):563-77. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0338-z. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18665350
-
Excitatory synchronization of rat hippocampal interneurons during network activation in vitro.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 9;17:1129991. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1129991. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36970420 Free PMC article.
-
The LIM homeodomain protein Lhx6 regulates maturation of interneurons and network excitability in the mammalian cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Aug;23(8):1811-23. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs159. Epub 2012 Jun 17. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22710612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acuna-Goycolea C, Tamamaki N, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, van den Pol AN. Mechanisms of neuropeptide Y, peptide YY, and pancreatic polypeptide inhibition of identified green fluorescent protein-expressing GABA neurons in the hypothalamic neuroendocrine arcuate nucleus. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7406–7419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akaike N. Gramicidin perforated patch recording and intracellular chloride activity in excitable cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1996;65:251–264. Review. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG. A Golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978;182:851–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

