Obestatin partially affects ghrelin stimulation of food intake and growth hormone secretion in rodents
- PMID: 17204551
- PMCID: PMC1890395
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2006-1231
Obestatin partially affects ghrelin stimulation of food intake and growth hormone secretion in rodents
Abstract
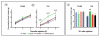
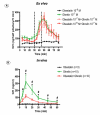
Administration of ghrelin, an endogenous ligand for the GH secretagogue receptor 1a (GHSR 1a), induces potent stimulating effects on GH secretion and food intake. However, more than 7 yr after its discovery, the role of endogenous ghrelin remains elusive. Recently, a second peptide, obestatin, also generated from proteolytic cleavage of preproghrelin has been identified. This peptide inhibits food intake and gastrointestinal motility but does not modify in vitro GH release from pituitary cells. In this study, we have reinvestigated obestatin functions by measuring plasma ghrelin and obestatin levels in a period of spontaneous feeding in ad libitum-fed and 24-h fasted mice. Whereas fasting resulted in elevated ghrelin levels, obestatin levels were significantly reduced. Exogenous obestatin per se did not modify food intake in fasted and fed mice. However, it inhibited ghrelin orexigenic effect that were evident in fed mice only. The effects of obestatin on GH secretion were monitored in superfused pituitary explants and in freely moving rats. Obestatin was only effective in vivo to inhibit ghrelin stimulation of GH levels. Finally, the relationship between octanoylated ghrelin, obestatin, and GH secretions was evaluated by iterative blood sampling every 20 min during 6 h in freely moving adult male rats. The half-life of exogenous obestatin (10 microg iv) in plasma was about 22 min. Plasma obestatin levels exhibited an ultradian pulsatility with a frequency slightly lower than octanoylated ghrelin and GH. Ghrelin and obestatin levels were not strictly correlated. In conclusion, these results show that obestatin, like ghrelin, is secreted in a pulsatile manner and that in some conditions; obestatin can modulate exogenous ghrelin action. It remains to be determined whether obestatin modulates endogenous ghrelin actions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neither intravenous nor intracerebroventricular administration of obestatin affects the secretion of GH, PRL, TSH and ACTH in rats.Regul Pept. 2007 Feb 1;138(2-3):141-4. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2006.09.001. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Regul Pept. 2007. PMID: 17055593
-
Obestatin inhibits feeding but does not modulate GH and corticosterone secretion in the rat.J Endocrinol Invest. 2006 Sep;29(8):RC16-8. doi: 10.1007/BF03344175. J Endocrinol Invest. 2006. PMID: 17033254
-
The ghrelin/obestatin balance in the physiological and pathological control of growth hormone secretion, body composition and food intake.J Neuroendocrinol. 2010 Jul;22(7):793-804. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02019.x. Epub 2010 May 6. J Neuroendocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20456603 Review.
-
Ghrelin stimulates GH but not food intake in arcuate nucleus ablated rats.Endocrinology. 2002 Sep;143(9):3268-75. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220268. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 12193538
-
Lack of obestatin effects on food intake: should obestatin be renamed ghrelin-associated peptide (GAP)?Regul Pept. 2007 Jun 7;141(1-3):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2006.12.023. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Regul Pept. 2007. PMID: 17321609 Review.
Cited by
-
Obestatin is associated to muscle strength, functional capacity and cognitive status in old women.Age (Dordr). 2013 Dec;35(6):2515-23. doi: 10.1007/s11357-013-9532-0. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Age (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 23604919 Free PMC article.
-
Biological effects of obestatin.Endocrine. 2011 Jun;39(3):205-11. doi: 10.1007/s12020-011-9453-6. Epub 2011 Mar 20. Endocrine. 2011. PMID: 21424587 Review.
-
Pretreatment with obestatin inhibits the development of acetic acid-induced colitis in rats.Arch Med Sci. 2018 Jun;14(4):920-929. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.58749. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Arch Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30002711 Free PMC article.
-
Obestatin stimulates glucose-induced insulin secretion through ghrelin receptor GHS-R.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 20;7(1):979. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00888-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28428639 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Ghrelin System in Colitis and Hepatitis as Risk Factors for Inflammatory-Related Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 23;23(19):11188. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911188. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–660. - PubMed
-
- Arvat E, Maccario M, Di Vito L, Broglio F, Benso A, Gottero C, Papotti M, Muccioli G, Dieguez C, Casanueva FF, Deghenghi R, Camanni F, Ghigo E. Endocrine activities of ghrelin, a natural growth hormone secretagogue (GHS), in humans: comparison and interactions with hexarelin, a nonnatural peptidyl GHS, and GH-releasing hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:1169–1174. - PubMed
-
- Tolle V, Zizzari P, Tomasetto C, Rio MC, Epelbaum J, Bluet-Pajot MT. In vivo and in vitro effects of ghrelin/motilin-related peptide on growth hormone secretion in the rat. Neuroendocrinology. 2001;73:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Nakazato M, Murakami N, Date Y, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K, Matsukura S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature. 2001;409:194–198. - PubMed
-
- Tolle V, Bassant MH, Zizzari P, Poindessous-Jazat F, Tomasetto C, Epelbaum J, Bluet-Pajot MT. Ultradian rhythmicity of ghrelin secretion in relation with GH, feeding behavior, and sleep-wake patterns in rats. Endocrinology. 2002;143:1353–1361. - PubMed

