Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3
- PMID: 17206155
- PMCID: PMC3025857
- DOI: 10.1038/nature05474
Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3
Abstract
Oncogenic tyrosine kinases have proved to be promising targets for the development of highly effective anticancer drugs. However, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) against the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) family show only limited activity against HER2-driven breast cancers, despite effective inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and HER2 in vivo. The reasons for this are unclear. Signalling in trans is a key feature of this multimember family and the critically important phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase (PI(3)K)/Akt pathway is driven predominantly through transphosphorylation of the kinase-inactive HER3 (refs 9, 10). Here we show that HER3 and consequently PI(3)K/Akt signalling evade inhibition by current HER-family TKIs in vitro and in tumours in vivo. This is due to a compensatory shift in the HER3 phosphorylation-dephosphorylation equilibrium, driven by increased membrane HER3 expression driving the phosphorylation reaction and by reduced HER3 phosphatase activity impeding the dephosphorylation reaction. These compensatory changes are driven by Akt-mediated negative-feedback signalling. Although HER3 is not a direct target of TKIs, HER3 substrate resistance undermines their efficacy and has thus far gone undetected. The experimental abrogation of HER3 resistance by small interfering RNA knockdown restores potent pro-apoptotic activity to otherwise cytostatic HER TKIs, re-affirming the oncogene-addicted nature of HER2-driven tumours and the therapeutic promise of this oncoprotein target. However, because HER3 signalling is buffered against an incomplete inhibition of HER2 kinase, much more potent TKIs or combination strategies are required to silence oncogenic HER2 signalling effectively. The biologic marker with which to assess the efficacy of HER TKIs should be the transphosphorylation of HER3 rather than autophosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

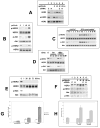
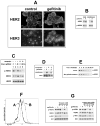

References
-
- Winer EP, Cobleigh M, Dickler M, Miller K, Fehrehbacher L, Jones CM, Anderson S, Eberhard D, Jones C. Phase II multicenter study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tarceva (Erlotinib HCl, OSI-774) in women with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. San Antonio Br Can Symp. 2002:445.
-
- Blackwell K, Kaplan EH, Franco SX, Marcom PK, Maleski MJ, Sorenson MS, Berger MS. A phase II, open-label, multicenter study of GW572016 in patients with trastuzumab-refractory metastatic breast cancer. Proc Amer Soc Clin Onc. 2004:3006.
-
- Dees EC, Burris HA, Hurwitz H, Dowlati A, Smith D, Kock KM, Stead A, Mangum S, Harris JL, Spector N. Clinical summary of 67 heavily pre-treated patients with metastatic carcinomas treated with GW572016 in a phase Ib study. Proc Amer Soc Clin Onc. 2004:3188.
-
- Campos SM, Seiden MV, Oza A, Plante M, Potkul R, Hamid O, Lenehan P, Kaldjian E, Jordan C, Hirte H. A phase 2, single agent study of CI-1033 administered at two doses in ovarian cancer patients who failed platinum therapy. Proc Amer Soc Clin Onc. 2004:5054.
-
- Baselga J, et al. Phase II and tumor pharmacodynamic study of gefitinib in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5323–5333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

