Multifunctional polyelectrolyte multilayer films: combining mechanical resistance, biodegradability, and bioactivity
- PMID: 17206799
- PMCID: PMC2535908
- DOI: 10.1021/bm060765k
Multifunctional polyelectrolyte multilayer films: combining mechanical resistance, biodegradability, and bioactivity
Abstract
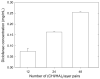
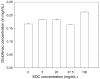
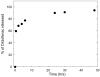
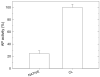
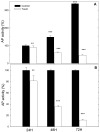
Cross-linked polyelectrolyte multilayer films (CL PEM) have an increased rigidity and are mechanically more resistant than native (e.g., uncrosslinked) films. However, they are still biodegradable, which make them interesting candidates for biomedical applications. In this study, CL PEM films have been explored for their multifunctional properties as (i) mechanically resistant, (ii) biodegradable, and (iii) bioactive films. Toward this end, we investigated drug loading into CL chitosan/hyaluronan (CHI/HA) and poly(L-lysine)/hyaluronan (PLL/HA) films by simple diffusion of the drugs. Sodium diclofenac and paclitaxel were chosen as model drugs and were successfully loaded into the films. The effect of varying the number of layers in the (CHI/HA) films as well as the cross-linker concentration on diclofenac loading were studied. Diclofenac was released from the film in about 10 h. Paclitaxel was also found to diffuse within CL films. Its activity was maintained after loading in the CL films, and cellular viability could be reduced by about 55% over 3 days. Such a simple approach may be applied to other types of cross-linked films and to other drugs. These results prove that it is possible to design multifunctional multilayer films that combine mechanical resistance, biodegradability, and bioactivity properties into a single PEM architecture.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elasticity of native and cross-linked polyelectrolyte multilayer films.Biomacromolecules. 2004 Sep-Oct;5(5):1908-16. doi: 10.1021/bm0498023. Biomacromolecules. 2004. PMID: 15360305
-
Polyelectrolyte multilayer films as substrates for photoreceptor cells.Biomacromolecules. 2006 Jan;7(1):86-94. doi: 10.1021/bm0505134. Biomacromolecules. 2006. PMID: 16398502
-
Elasticity, biodegradability and cell adhesive properties of chitosan/hyaluronan multilayer films.Biomed Mater. 2007 Mar;2(1):S45-51. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/2/1/S07. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Biomed Mater. 2007. PMID: 18458419
-
Gradients of physical and biochemical cues on polyelectrolyte multilayer films generated via microfluidics.Lab Chip. 2013 Apr 21;13(8):1562-70. doi: 10.1039/c3lc41407h. Lab Chip. 2013. PMID: 23440074 Free PMC article.
-
Polyelectrolyte multilayer films: from physico-chemical properties to the control of cellular processes.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(7):685-97. doi: 10.2174/092986708783885219. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18336282 Review.
Cited by
-
Binding Mechanism of the Model Charged Dye Carboxyfluorescein to Hyaluronan/Polylysine Multilayers.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Nov 8;9(44):38908-38918. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b12449. Epub 2017 Oct 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 29035502 Free PMC article.
-
Tailored Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Systems by Variation of Polyelectrolyte Composition and EDC/NHS Cross-Linking: Controlled Drug Release vs. Drug Reservoir Capabilities and Cellular Response for Improved Osseointegration.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;14(20):4315. doi: 10.3390/polym14204315. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297892 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Synthetic Polymer-Based Polyelectrolyte LbL Coating Assembly on Surface Treated AZ31-Mg Alloys.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jan 29;14(2):75. doi: 10.3390/jfb14020075. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36826874 Free PMC article.
-
Polyelectrolyte multilayer films of controlled stiffness modulate myoblast cells differentiation.Adv Funct Mater. 2008;18(9):1378-1389. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200701297. Adv Funct Mater. 2008. PMID: 18841249 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue integration of growth factor-eluting layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte multilayer coated implants.Biomaterials. 2011 Feb;32(5):1446-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.052. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21084117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seal BL, Otero TC, Panitch A. Mat Sci Eng C. 2001;34:147–230.
-
- Whittlesey KJ, Shea LD. Experimental Neuroogyl. 2004;190:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y, Prestwich GD. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2002;2:209–226. - PubMed
-
- Prestwich GD, Marecak DM, Marecek JF, Vercruysse KP, Ziebell MR. J Control Release. 1998;53:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Decher G. Science. 1997;277:1232–1237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

