Pathway of biogenesis of apolipoprotein E-containing HDL in vivo with the participation of ABCA1 and LCAT
- PMID: 17206937
- PMCID: PMC1874240
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061048
Pathway of biogenesis of apolipoprotein E-containing HDL in vivo with the participation of ABCA1 and LCAT
Abstract
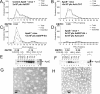
We have investigated the ability of apoE (apolipoprotein E) to participate in the biogenesis of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) particles in vivo using adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in apoA-I-/- (apolipoprotein A-I) or ABCA1-/- (ATP-binding cassette A1) mice. Infection of apoA-I-/- mice with 2x10(9) pfu (plaque-forming units) of an apoE4-expressing adenovirus increased both HDL and the triacylglycerol-rich VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein)/IDL (intermediate-density lipoprotein)/LDL (low-density lipoprotein) fraction and generated discoidal HDL particles. ABCA1-/- mice treated similarly failed to form HDL particles, suggesting that ABCA1 is essential for the generation of apoE-containing HDL. Combined infection of apoA-I-/- mice with a mixture of adenoviruses expressing both apoE4 (2x10(9) pfu) and human LCAT (lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase) (5x10(8) pfu) cleared the triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins, increased HDL and converted the discoidal HDL into spherical HDL. Similarly, co-infection of apoE-/- mice with apoE4 and human LCAT corrected the hypercholesterolaemia and generated spherical particles, suggesting that LCAT is essential for the maturation of apoE-containing HDL. Overall, the findings indicate that apoE has a dual functionality. In addition to its documented functions in the clearance of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins, it participates in the biogenesis of HDL-sized apoE-containing particles. HDL particles generated by this pathway may account at least for some of the atheroprotective functions of apoE.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Discrete roles of apoA-I and apoE in the biogenesis of HDL species: lessons learned from gene transfer studies in different mouse models.Ann Med. 2008;40 Suppl 1:14-28. doi: 10.1080/07853890701687219. Ann Med. 2008. PMID: 18246469 Review.
-
Domains of apoE4 required for the biogenesis of apoE-containing HDL.Ann Med. 2011 Jun;43(4):302-11. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2010.549143. Ann Med. 2011. PMID: 21604997 Free PMC article.
-
Substitutions of glutamate 110 and 111 in the middle helix 4 of human apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) by alanine affect the structure and in vitro functions of apoA-I and induce severe hypertriglyceridemia in apoA-I-deficient mice.Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 17;43(32):10442-57. doi: 10.1021/bi049782p. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15301543
-
Naturally occurring and bioengineered apoA-I mutations that inhibit the conversion of discoidal to spherical HDL: the abnormal HDL phenotypes can be corrected by treatment with LCAT.Biochem J. 2007 Aug 15;406(1):167-74. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070296. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17506726 Free PMC article.
-
Role of apoA-I, ABCA1, LCAT, and SR-BI in the biogenesis of HDL.J Mol Med (Berl). 2006 Apr;84(4):276-94. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0030-4. Epub 2006 Feb 25. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16501936 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular bases of copper and iron deficiency-associated dyslipidemia: a microarray analysis of the rat intestinal transcriptome.Genes Nutr. 2010 Mar;5(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s12263-009-0153-2. Epub 2009 Oct 11. Genes Nutr. 2010. PMID: 19821111 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal alpha-helix domain of apolipoprotein E is required for interaction with nonstructural protein 5A and assembly of hepatitis C virus.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):11532-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01021-10. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20719944 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of HDL's to piHDL's Proteome in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Diseases, and HDL-Targeted Therapies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;15(10):1278. doi: 10.3390/ph15101278. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An apoA-I mimetic peptide increases LCAT activity in mice through increasing HDL concentration.Int J Biol Sci. 2009 Jul 28;5(5):489-99. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5.489. Int J Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19680471 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoproteins E and CIII interact to regulate HDL metabolism and coronary heart disease risk.JCI Insight. 2018 Feb 22;3(4):e98045. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.98045. eCollection 2018 Feb 22. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 29467335 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Zannis V. I., Kypreos K. E., Chroni A., Kardassis D., Zanni E. E. Lipoproteins and atherogenesis. In: Loscalzo J., editor. Molecular Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis. New York: Taylor & Francis; 2004. pp. 111–174.
-
- Zannis V. I., Zanni E. E., Makrides S. C., Kardassis D., Aleshkov S. Role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease. In: Catravas J. D., editor. NATO ASI Series, Life Sciences. New York: Plenum Press; 1998. pp. 179–209.
-
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setala K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992;71:343–353. - PubMed
-
- Linton M. F., Fazio S. Macrophages, lipoprotein metabolism, and atherosclerosis: insights from murine bone marrow transplantation studies. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1999;10:97–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

