Clinical relevance of neutral endopeptidase (NEP/CD10) in melanoma
- PMID: 17207277
- PMCID: PMC1770905
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-5-2
Clinical relevance of neutral endopeptidase (NEP/CD10) in melanoma
Abstract
Background: Overexpression of Neutral Endopeptidase (NEP) has been reported in metastatic carcinomas, implicating NEP in tumor progression and suggesting a role for NEP inhibitors in its treatment. We investigated the role of NEP expression in the clinical progression of cutaneous melanoma.
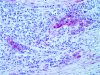
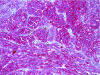
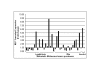
Methods: We screened 7 melanoma cell lines for NEP protein expression. NEP-specific siRNA was transfected into the lines to examine the role of gene transcription in NEP expression. Immunohistochemistry was done for 93 specimens and correlated with clinicopathologic parameters. Thirty-seven metastatic melanoma specimens were examined for NEP transcript expression using Affymetrix GeneChips. In a subset of 25 specimens for which both transcript and protein expression was available, expression ratios were used to identify genes that co-express with NEP in GeneChip analysis.
Results: NEP was overexpressed in 4/7 human melanoma cell lines, and siRNA knock-down of NEP transcripts led to downregulation of its protein expression. NEP protein overexpression was significantly more common in metastatic versus primary tumors (P = 0.002). Twelve of 37 (32%) metastatic tumors had increased NEP transcript expression, and an association was observed between NEP transcript upregulation and protein overexpression (P < 0.0001). Thirty-eight genes were found to significantly co-express with NEP (p < 0.005). Thirty-three genes positively correlated with NEP, including genes involved in the MAP kinase pathway, antigen processing and presentation, apoptosis, and WNT signaling pathway, and 5 genes negatively correlated with NEP, including genes of focal adhesion and the notch signaling pathways.
Conclusion: NEP overexpression, which seems to be largely driven by increased transcription, is rare in primary melanoma and occurs late in melanoma progression. Functional studies are needed to better understand the mechanisms of NEP regulation in melanoma.
Figures
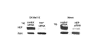
References
-
- Day AL, Wick E, Jordan TH, Jaffray CE, Bunnett NW, Grady EF, Kirkwood KS. Neutral endopeptidase determines the severity of pancreatitis-associated lung injury. J Surg Res. 2005;128:21–27. - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Califf RM, Konstam MA, Krum H, McMurray JJ, Rouleau JL, Swedberg K. Comparison of omapatrilat and enalapril in patients with chronic heart failure: the Omapatrilat Versus Enalapril Randomized Trial of Utility in Reducing Events (OVERTURE) Circulation. 2002;106:920–926. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000029801.86489.50. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cohen AJ, Bunn PA, Franklin W, Magill-Solc C, Hartmann C, Helfrich B, Gilman L, Folkvord J, Helm K, Miller YE. Neutral endopeptidase: variable expression in human lung, inactivation in lung cancer, and modulation of peptide-induced calcium flux. Cancer Res. 1996;56:831–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

