Green tea increases anti-inflammatory tristetraprolin and decreases pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor mRNA levels in rats
- PMID: 17207279
- PMCID: PMC1783848
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-4-1
Green tea increases anti-inflammatory tristetraprolin and decreases pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor mRNA levels in rats
Abstract
Background: Tristetraprolin (TTP/ZFP36) family proteins have anti-inflammatory activity by binding to and destabilizing pro-inflammatory mRNAs such as Tnf mRNA, and represent a potential therapeutic target for inflammation-related diseases. Tea has anti-inflammatory properties but the molecular mechanisms have not been completely elucidated. We hypothesized that TTP and/or its homologues might contribute to the beneficial effects of tea as an anti-inflammatory product.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR was used to investigate the effects of green tea (0, 1, and 2 g solid extract/kg diet) on the expression of Ttp family genes (Ttp/Tis11/Zfp36, Zfp36l1/Tis11b, Zfp36l2/Tis11d, Zfp36l3), pro-inflammatory genes (Tnf, Csf2/Gm-csf, Ptgs2/Cox2), and Elavl1/Hua/Hur and Vegf genes in liver and muscle of rats fed a high-fructose diet known to induce insulin resistance, oxidative stress, inflammation, and TNF-alpha levels.
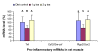
Results: Ttp and Zfp36l1 mRNAs were the major forms in both liver and skeletal muscle. Ttp, Zfp36l1, and Zfp36l2 mRNA levels were more abundant in the liver than those in the muscle. Csf2/Gm-csf and Zfp36l3 mRNAs were undetectable in both tissues. Tea (1 g solid extract/kg diet) increased Ttp mRNA levels by 50-140% but Tnf mRNA levels decreased by 30% in both tissues, and Ptgs2/Cox2 mRNA levels decreased by 40% in the muscle. Tea (2 g solid extract/kg diet) increased Elavl1/Hua/Hur mRNA levels by 40% in the liver but did not affect any of the other mRNA levels in liver or muscle.
Conclusion: These results show that tea can modulate Ttp mRNA levels in animals and suggest that a post-transcriptional mechanism through TTP could partially account for tea's anti-inflammatory properties. The results also suggest that drinking adequate amounts of green tea may play a role in the prevention of inflammation-related diseases.
Figures
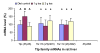
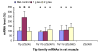
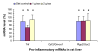
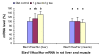
Similar articles
-
Insulin increases tristetraprolin and decreases VEGF gene expression in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Jun;16(6):1208-18. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.65. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008. PMID: 18388887
-
Lipopolysaccharide regulation of antiinflammatory tristetraprolin family and proinflammatory gene expression in mouse macrophages.BMC Res Notes. 2024 Mar 19;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13104-024-06743-6. BMC Res Notes. 2024. PMID: 38504371 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamon polyphenol extract regulates tristetraprolin and related gene expression in mouse adipocytes.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Mar 23;59(6):2739-44. doi: 10.1021/jf103527x. Epub 2011 Feb 17. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21329350
-
Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Diseases by RNA-Binding ZFP36 Family Proteins.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;12:711633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711633. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of TTP and HuR plays an important role in cancers.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):14451-14461. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5397-z. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27644249 Review.
Cited by
-
Iranian black tea and cowslip extracts induce tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion from mouse macrophage cell culture.Iran J Pharm Res. 2010 Winter;9(1):83-7. Iran J Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 24363711 Free PMC article.
-
Tea consumption and physical function in older adults: a cross-sectional study.J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(2):161-6. doi: 10.1007/s12603-013-0354-7. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014. PMID: 24522468
-
Cottonseed extracts regulate gene expression in human colon cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 20;12(1):1039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05030-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35058516 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of green tea supplementation on inflammation markers, antioxidant status and blood pressure in NaCl-induced hypertensive rat model.Food Nutr Res. 2017 Mar 3;61(1):1295525. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1295525. eCollection 2017. Food Nutr Res. 2017. PMID: 28326006 Free PMC article.
-
The role of tristetraprolin in cancer and inflammation.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(1):174-88. doi: 10.2741/3920. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lai WS, Stumpo DJ, Blackshear PJ. Rapid insulin-stimulated accumulation of an mRNA encoding a proline-rich protein. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:16556–16563. - PubMed
-
- DuBois RN, McLane MW, Ryder K, Lau LF, Nathans D. A growth factor-inducible nuclear protein with a novel cysteine/histidine repetitive sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:19185–19191. - PubMed
-
- Varnum BC, Lim RW, Kujubu DA, Luner SJ, Kaufman SE, Greenberger JS, Gasson JC, Herschman HR. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate induce a distinct, restricted subset of primary- response TIS genes in both proliferating and terminally differentiated myeloid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989;9:3580–3583. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

