Changes in estrogen receptor-alpha mRNA in the mouse cortex during development
- PMID: 17207781
- PMCID: PMC3443600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.11.069
Changes in estrogen receptor-alpha mRNA in the mouse cortex during development
Abstract
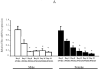
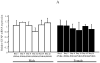
Estrogen plays a critical role in brain development and is responsible for generating sex differences in cognition and emotion. Studies in rodent models have shown high levels of estrogen binding in non-reproductive areas of the brain during development, including the cortex and hippocampus, yet binding is diminished in the same areas of the adult brain. These binding studies demonstrated that estrogen receptors decline in the cortex during development but did not identify which of the two estrogen receptors was present. In the current study, we examined the expression of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) in the mouse cortex during the first month of life. Messenger RNA was isolated from cortical tissue taken from C57BL/6 mice on postnatal day (PND) 1, 4, 10, 18 and 25 and expression levels were determined by real-time PCR. ERalpha mRNA expression in the mouse cortex at PND 25 was significantly reduced as compared to PND 1 (p<0.01). ERbeta mRNA expression at PND 25 was significantly increased as compared to PND 1 (p<0.05). Although the increase in ERbeta mRNA was statistically significant, the ERbeta levels were extremely low in the isocortex compared to ERalpha mRNA levels, suggesting that ERalpha may play a more critical role in the developmental decrease of estradiol binding than ERbeta. Additionally, we measured ERalpha mRNA expression in organotypic explant cultures of cortex taken from PND 3 mice. Explants were maintained in vitro for 3 weeks. mRNA was isolated at several time points and ERalpha and ERbeta mRNA was measured by real-time RT-PCR. ERalpha and ERbeta mRNA levels reflected a similar pattern in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that signals outside the cortex are not needed for this developmental change. This study lays the groundwork for an understanding of the mechanisms of the developmental regulation of ERalpha mRNA.
Figures
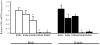
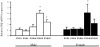



Similar articles
-
Gene expression profile of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in rat brain during aging and following high fat diet.C R Biol. 2017 Aug;340(8):372-378. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2017.08.001. Epub 2017 Aug 30. C R Biol. 2017. PMID: 28869142
-
Regional, laminar and cellular distribution of immunoreactivity for ERbeta in the cerebral cortex of hormonally intact, postnatally developing male and female rats.Cereb Cortex. 2006 Aug;16(8):1181-92. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhj059. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Cereb Cortex. 2006. PMID: 16221921
-
Transcription of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in mouse cerebral cortex: effect of age, sex, 17beta-estradiol and testosterone.Neurochem Int. 2007 Jan;50(2):314-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2006.08.019. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Neurochem Int. 2007. PMID: 17113197
-
Estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression in the cortex: sex differences during development and in adulthood.Horm Behav. 2011 Mar;59(3):353-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 20713055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of oestrogen receptor gene expression: new insights and novel mechanisms.J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Mar;21(4):238-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01830.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19207817 Review.
Cited by
-
Estradiol: a hormone with diverse and contradictory neuroprotective actions.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2009;11(3):297-303. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2009.11.3/pmwise. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19877497 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of an estrogen receptor alpha-iCre knock-in mouse.Genesis. 2017 Dec;55(12):10.1002/dvg.23084. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23084. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Genesis. 2017. PMID: 29115049 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation and demethylation shape sexual differentiation of neurochemical phenotype.Horm Behav. 2023 May;151:105349. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2023.105349. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Horm Behav. 2023. PMID: 37001316 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of the estrogen receptor alpha promoter in the cerebral cortex following ischemia in male and female rats.Neuroscience. 2008 Apr 9;152(4):982-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.048. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18353557 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic impacts of endocrine disruptors in the brain.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2017 Jan;44:1-26. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27663243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amin Z, Canli T, Epperson CN. Effect of estrogen-serotonin interactions on mood and cognition. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev. 2005;4:43–58. - PubMed
-
- Arnold AP, Breedlove SM. Organizational and activational effects of sex steroids on brain and behavior: a reanalysis. Horm Behav. 1985;19:469–98. - PubMed
-
- Azcoitia I, Sierra A, Garcia-Segura LM. Localization of estrogen receptor beta-immunoreactivity in astrocytes of the adult rat brain. Glia. 1999;26:260–7. - PubMed
-
- Bakker J, De Mees C, Douhard Q, Balthazart J, Gabant P, Szpirer J, Szpirer C. Alpha-fetoprotein protects the developing female mouse brain from masculinization and defeminization by estrogens. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:220–6. - PubMed
-
- Bakker J, van Ophemert J, Slob AK. Organization of partner preference and sexual behavior and its nocturnal rhythmicity in male rats. Behav Neurosci. 1993;107:1049–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

