Behavioral effects of the R-(+)- and S-(-)-enantiomers of the dopamine D(1)-like partial receptor agonist SKF 83959 in monkeys
- PMID: 17207791
- PMCID: PMC2447824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.11.042
Behavioral effects of the R-(+)- and S-(-)-enantiomers of the dopamine D(1)-like partial receptor agonist SKF 83959 in monkeys
Erratum in
- Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec 1;575(1-3):187
Abstract
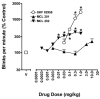
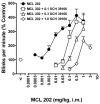
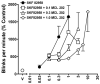
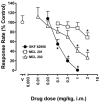
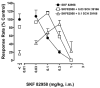
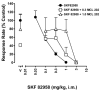
Dopamine D(1)-like partial receptor agonists such as SKF 83959 have been proposed as potential candidates for the treatment of cocaine addiction. The present studies were conducted to further characterize SKF 83959 by pharmacologically evaluating effects of its R-(+)- and S-(-)-enantiomers, MCL 202 and MCL 201, respectively, on overt behavior (eye blinking) and schedule-controlled performance in squirrel monkeys. MCL 202, like the D(1) full receptor agonist SKF 82958, produced dose-related increases in eye blinking and decreases in rates of fixed-ratio responding. However, the magnitude of effects of MCL 202 on eye blinking was less than observed with SKF 82958. In contrast to the effects of its R-(+) enantiomer, MCL 201 was relatively devoid of behavioral activity up to doses that were approximately 10-fold greater than MCL 202. Pretreatment with the selective D(1)-like receptor antagonist SCH 39166 dose-dependently antagonized increases in eye blinking produced by MCL 202, confirming the involvement of D(1) mechanisms in its effects. A dose-ratio analysis of the antagonism of effects of MCL 202 by SCH 39166 revealed an apparent pA(2) value of 7.675 with a slope of -0.78+/-0.04. In further studies, pretreatment with MCL 202 antagonized the effects of SKF 82958 on eye blinking and, like SCH 39166, schedule-controlled behavior in a dose-related manner. A dose-ratio analysis of the antagonist effects of MCL 202 on the SKF 82958-induced increases in eye blinking revealed ratios of 2.7, 4.8 and 31.1 for 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg dose of the antagonist, respectively, indicative of a significant change in the potency of SKF 82958. These results suggest that MCL 202, like its parent compound SKF 83959, has both D(1) receptor-mediated agonist and antagonist properties, consistent with its characterization as a partial agonist at the D(1)-like receptor. In addition, the inactivity of MCL 201, the S-(-)-enantiomer, suggests that the behavioral effects of SKF 83959 can be attributed primarily to the activity of its R-(+)-enantiomer.
Figures
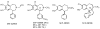
References
-
- Abrahams BS, Rutherford JD, Mallet PE, Beninger RJ. Place conditioning with the dopamine D1-like receptor agonist SKF 82958 but not SKF 81297 or SKF 77434. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;343:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Abrahams BS, Rutherford JD, Mallet PE, Beninger RJ. Place conditioning with dopamine D1 and D2 agonists injected peripherally or into nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology. 1998;103:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Andersen PH, Jansen JA. Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;188:335–347. - PubMed
-
- Andringa G, Stoof JC, Cools AR. Sub-chronic administration of the dopamine D1 antagonist SKF 83959 in bilaterally MPTP-treated rhesus monkeys: stable therapeutic effects and wearing-off dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology. 1999;146:328–334. - PubMed
-
- Andringa G, Drukarch B, Leysen JE, Cools AR, Stoof JC. The alleged dopamine D1 receptor agonist SKF 83959 is a dopamine D1 receptor antagonist in primate cells and interacts with other receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;364:33–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

