Btk regulates multiple stages in the development and survival of B-1 cells
- PMID: 17207856
- PMCID: PMC2567238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.11.023
Btk regulates multiple stages in the development and survival of B-1 cells
Abstract
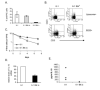
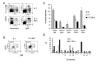
B-1 cells are important players in the first line of defense against pathogens. According to current models for the origin of B-1 cells, they either represent a separate lineage from conventional B-2 cells or differentiate from conventional B-2 cells via an intermediate, B-1(int), in response to positive selection by antigen. Here we show that Btk, a Tec family kinase that mediates B cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling, is required at multiple stages of B-1 cell development. VH12 anti-phosphatidylcholine (PtC) IgH transgenic mice provide a model for the induced differentiation of B-1 cells. This transgene selects for PtC-reactive cells and induces them to adopt a B-1 phenotype. Both processes have been shown to depend on Btk. To determine whether this is secondary to a requirement for Btk in the development of mature B-2 cells, we crossed VH12 transgenic mice to mice expressing low levels of Btk. B-2 cell development occurs normally in Btk(lo) mice despite reduced responsiveness to BCR crosslinking. Analysis of VH12.Btk(lo) mice reveals that Btk regulates the B-1(int) to B-1 transition and/or the survival of splenic B-1 cells, in part via a mechanism independent of its role in BCR signaling. We also show that Btk mediates the survival of, and expression of IL-10 by, those B-1 cells that do develop and migrate to the peritoneum. Multiple roles for Btk in B-1 cell development and maintenance may explain the particular sensitivity of this population to mutations in components of Btk signaling pathways.
Figures
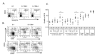



Similar articles
-
Function of Bruton's tyrosine kinase during B cell development is partially independent of its catalytic activity.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 1;171(11):5988-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.5988. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14634110
-
Btk function in B cell development and response.Semin Immunol. 1998 Aug;10(4):309-16. doi: 10.1006/smim.1998.0123. Semin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9695187 Review.
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase is required for signaling the CD79b-mediated pro-B to pre-B cell transition.Int Immunol. 2001 Apr;13(4):485-93. doi: 10.1093/intimm/13.4.485. Int Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11282988
-
Independent and opposing roles for Btk and lyn in B and myeloid signaling pathways.J Exp Med. 1998 Sep 7;188(5):833-44. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.5.833. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9730885 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase controls a sustained calcium signal essential for B lineage development and function.Clin Immunol. 1999 Jun;91(3):243-53. doi: 10.1006/clim.1999.4732. Clin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10370369 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of B cell receptor signaling in IL-10 production by normal and malignant B-1 cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Dec;1362(1):239-249. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12802. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26096907 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase, a Component of B Cell Signaling Pathways, Has Multiple Roles in the Pathogenesis of Lupus.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 22;8:1986. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01986. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29403475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors in HIV-1-infected cells.J Neurovirol. 2015 Jun;21(3):257-75. doi: 10.1007/s13365-015-0323-5. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Neurovirol. 2015. PMID: 25672887 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: The Next Frontier of B-Cell-Targeted Therapies for Cancer, Autoimmune Disorders, and Multiple Sclerosis.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 18;11(20):6139. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206139. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Drives Btk-Mediated Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 30;10:95. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00095. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30761150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansel KM, Harris RB, Cyster JG. CXCL13 is required for B1 cell homing, natural antibody production, and body cavity immunity. Immunity. 2002;16:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Arnold LW, McCray SK, Tatu C, Clarke SH. Identification of a precursor to phosphatidyl choline-specific B-1 cells suggesting that B-1 cells differentiate from splenic conventional B cells in vivo: cyclosporin A blocks differentiation to B-1. J Immunol. 2000;164:2924–2930. - PubMed
-
- Chan VW, Meng F, Soriano P, DeFranco AL, Lowell CA. Characterization of the B lymphocyte populations in Lyn-deficient mice and the role of Lyn in signal initiation and down-regulation. Immunity. 1997;7:69–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

