Differential regulation of RANTES and IL-8 expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 17207890
- PMCID: PMC1950237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.12.003
Differential regulation of RANTES and IL-8 expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells
Abstract
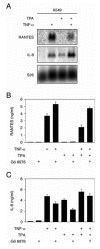
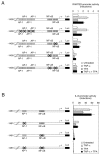
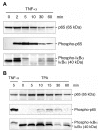
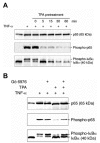
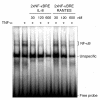
In lung adenocarcinoma, expression of Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed and presumably Secreted (RANTES) is a predictor of survival while that of interleukin (IL)-8 is associated with a poor prognosis. In several models, tumorigenesis is abolished by RANTES, while it is facilitated by IL-8. We studied the regulation of RANTES and IL-8 expression in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells. The effects of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and regulators of protein kinases C (PKC)alpha/beta were tested because these have been shown to modulate cancer development and progression. TNF-alpha stimulated expression of both chemokines, while the PKCalpha/beta activator 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate (TPA) induced only expression of IL-8 and inhibited TNF-alpha-induced RANTES expression. The PKCalpha/beta inhibitor Gö 6976 increased TNF-alpha-induced RANTES production and prevented its down-regulation by TPA. In contrast, it decreased TNF-alpha or TPA-induced IL-8 release. The differential regulation of RANTES and IL-8 expression was further analyzed. Site-directed mutagenesis indicated that regulation of RANTES promoter activity required two nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB response elements but not its activator protein (AP)-1 binding sites. An AP-1 and a NF-kappaB recognition sites were necessary for full induction of IL-8 promoter activity by TNF-alpha and TPA. Moreover, electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated that NF-kappaB response elements from the RANTES promoter were of lower affinity than that from the IL-8 promoter. Immunoblotting experiments showed that TPA was more potent than TNF-alpha to induce in a PKCalpha/beta dependent manner the p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling cascade which controls AP-1 activity. Conversely, TPA inhibited TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB signaling and was a weak activator of this pathway. Thus, TPA did not sufficiently activate NF-kappaB to increase transcription through the low affinity NF-kappaB binding sites on RANTES promoter and its inhibitory effect on TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB signaling resulted in a reduced transcription rate. On IL-8 promoter, increased transcription through the high affinity NF-kappaB binding site occurred even with poorly activated NF-kappaB and the functional AP-1 response element compensated any loss of transcription rate. These data provide a mechanistic insight into the differential regulation of IL-8 and RANTES expression by PKCalpha/beta in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Figures

References
-
- Garfinkel A. Cancer statistics and trends. In: Holleb AI, Fink DJ, Murphy GP, editors. American Cancer Society Textbook of Clinical Oncology. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 1991. pp. 2–9.
-
- Mountain CF. Lung cancer staging classification. Clin Chest Med. 1993;14(1):43–53. - PubMed
-
- Moran CJ, Arenberg DA, Huang CC, Giordano TJ, Thomas DG, Misek DE, Chen G, Iannettoni MD, Orringer MB, Hanash S, et al. RANTES expression is a predictor of survival in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8(12):3803–3812. - PubMed
-
- Mule JJ, Custer M, Averbook B, Yang JC, Weber JS, Goeddel DV, Rosenberg SA, Schall TJ. RANTES secretion by gene-modified tumor cells results in loss of tumorigenicity in vivo: role of immune cell subpopulations. Hum Gene Ther. 1996;7(13):1545–1553. - PubMed
-
- Kutubuddin M, Federoff HJ, Challita-Eid PM, Halterman M, Day B, Atkinson M, Planelles V, Rosenblatt JD. Eradication of pre-established lymphoma using herpes simplex virus amplicon vectors. Blood. 1999;93 (2):643–654. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

