ATP synthase--the structure of the stator stalk
- PMID: 17208001
- PMCID: PMC2570231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.12.006
ATP synthase--the structure of the stator stalk
Abstract
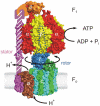
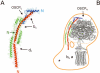
ATP synthase synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate using a unique rotary mechanism whereby two subcomplexes move relative to each other, powered by a proton or sodium gradient. The non-rotating parts of the machinery are held together by the "stator stalk". The recent resolution of the structure of a major portion of the stator stalk of mitochondrial ATP synthase represents an important step towards a structural model for the ATP synthase holoenzyme.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATP synthase: subunit-subunit interactions in the stator stalk.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Sep-Oct;1757(9-10):1162-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.04.007. Epub 2006 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16730323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rows of ATP synthase dimers in native mitochondrial inner membranes.Biophys J. 2007 Oct 15;93(8):2870-6. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.109728. Epub 2007 Jun 8. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17557793 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of human mitochondrial ATP synthase through two separate intermediates, F1-c-ring and b-e-g complex.FEBS Lett. 2015 Sep 14;589(19 Pt B):2707-12. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 20. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26297831
-
Structural organization of mitochondrial ATP synthase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jul-Aug;1777(7-8):592-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.04.027. Epub 2008 Apr 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18485888
-
The peripheral stalk of the mitochondrial ATP synthase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May-Jun;1757(5-6):286-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16697972 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis of the bloom-forming dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense exposed to Ginkgo biloba leaf extract, with an emphasis on photosynthesis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(12):18579-18592. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32409-8. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38351353
-
Role of Charged Residues in the Catalytic Sites of Escherichia coli ATP Synthase.J Amino Acids. 2011;2011:785741. doi: 10.4061/2011/785741. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 22312470 Free PMC article.
-
Parasite powerhouse: A review of the Toxoplasma gondii mitochondrion.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2022 Nov;69(6):e12906. doi: 10.1111/jeu.12906. Epub 2022 May 4. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35315174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystallization of the c14-rotor of the chloroplast ATP synthase reveals that it contains pigments.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jul-Aug;1777(7-8):605-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.05.009. Epub 2008 May 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18515064 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary primacy of sodium bioenergetics.Biol Direct. 2008 Apr 1;3:13. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-3-13. Biol Direct. 2008. PMID: 18380897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilkens S. Rotary molecular motors. Adv. Protein Chem. 2005;71:345–382. - PubMed
-
- Weber J, Senior AE. ATP synthesis driven by proton transport in F1F0-ATP synthase. FEBS Lett. 2003;545:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Capaldi RA, Aggeler R. Mechanism of the F1F0-type ATP synthase, a biological rotary motor. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:154–160. - PubMed
-
- Boyer PD. A research journey with ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:39045–39061. - PubMed
-
- Carbajo RJ, et al. Solution structure of subunit F6 from the peripheral stalk region of ATP synthase from bovine heart mitochondria. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;342:593–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

