Histone acetyltransferase p300 modulates gene expression in an epigenetic manner at high blood alcohol levels
- PMID: 17208223
- PMCID: PMC2753379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2006.10.006
Histone acetyltransferase p300 modulates gene expression in an epigenetic manner at high blood alcohol levels
Abstract
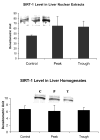
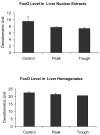
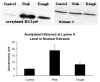
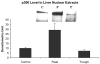
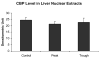
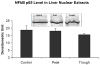
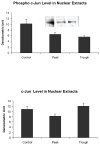
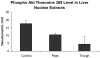
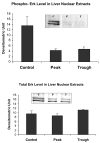
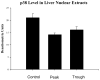
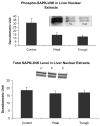
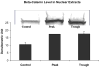
When rats are fed ethanol intragastrically at a constant rate for 1 month, the urinary alcohol level (UAL) cycles over 7-9 day intervals. At the peak UAL, the liver is hypoxic shifting the redox state to a reduced rate. Microarray analysis done on livers at the UAL peaks shows changes in approximately 1300 gene expression compared to the pair-fed controls. To determine the mechanism of the gene expression changes, histone acetylation regulation was investigated in liver nuclear extracts at the peaks and troughs of the UAL and their pair-fed controls. No change occurred in SirT-1. P300, a histone acetyltransferase (HAT), which acetylates histone H3 on lysine 9, was increased at the peaks. Histone 3 acetylated at lysine 9 was also increased at the peaks. This indicates that the up regulated genes at the UAL peaks resulted from an increase in p300 transcription regulation, epigenetically. P300 activates transcription of numerous genes in response to signal transcription factors such as H1F 1alpha, increased in the nucleus at UAL peaks. Signal transduction pathways, such as NFkappaB, AP-1, ERK, JNK, and p38 were not increased at the peaks. beta-Catenin was increased in the nuclear extract at the UAL troughs, where increased gene expression was absent. The increase in gene expression at the peaks was due, in part, to increased acetylation of histone 3 at lysine 9.
Figures
References
-
- Bardag-Gorce F, French BA, Li J, French SW. The blood alcohol level affects genes expression and transcription regulator proteins in an epigenetic manner. Hepatology. 2006:Abstract 1084.
-
- Bardag-Gorce F, French BA, Dedes J, Li J, French SW. Gene expression patterns of the liver in response to alcohol: In vitro and in vivo models compared. Exp Mol Pathol. 2006;80:241–251. - PubMed
-
- Bardag-Gorce F, French BA, Li J, Riley NE, Yuan QX, Reitz NE, Yuan QX, Reitz R, Cai Y, Wan Y-JY, French SW. The importance of cycling of blood alcohol levels in the pathogenesis of experimental alcoholic liver disease in rats fed ethanol intragastrically. Gastroenterology. 2002;13:325–35. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- French BA, Dedes J, Bardag-Gorce F, Li J, Wilson L, Fu P, Nan L, French SW. Microarray analysis of gene expression in the liver during the urinary ethanol cycle in rats fed ethanol intragastrically at a constant rate. Exp Mol Pathol. 2005;79:87–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

