Activated Ras induces cytoplasmic vacuolation and non-apoptotic death in glioblastoma cells via novel effector pathways
- PMID: 17210246
- PMCID: PMC1894854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.11.010
Activated Ras induces cytoplasmic vacuolation and non-apoptotic death in glioblastoma cells via novel effector pathways
Abstract
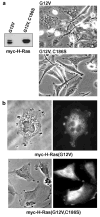
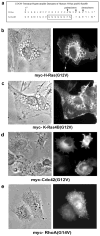
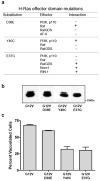
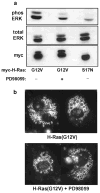
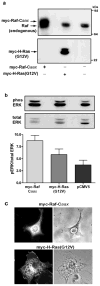
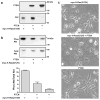
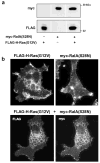
Expression of activated H-Ras induces a unique form of non-apoptotic cell death in human glioblastoma cells and other specific tumor cell lines. The major cytopathological features of this form of death are the accumulation of large phase-lucent, LAMP1-positive, cytoplasmic vacuoles. In this study we sought to determine if induction of cytoplasmic vacuolation a) depends on Ras farnesylation, b) is specific to H-Ras, and c) is mediated by signaling through the major known Ras effector pathways. We find that the unusual effects of activated H-Ras depend on farnesylation and membrane association of the GTPase. Both H-Ras(G12V) and K-Ras4B(G12V) stimulate vacuolation, but activated forms of Cdc42 and RhoA do not. Amino acid substitutions in the Ras effector domain, which are known to selectively impair its interactions with Raf kinase, class-I phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), or Ral nucleotide exchange factors, initially pointed to Raf as a possible mediator of cell vacuolation. However, the MEK inhibitor, PD98059, did not block the induction of vacuoles, and constitutively active Raf-Caax did not mimic the effects of Ras(G12V). Introduction of normal PTEN together with H-Ras(G12V) into U251 glioblastoma cells reduced the PI3K-dependent activation of Akt, but had no effect on vacuolation. Finally, co-expression of H-Ras(G12V) with a dominant-negative form of RalA did not suppress vacuolation. Taken together, the observations indicate that Ras activates non-conventional and perhaps unique effector pathways to induce cytoplasmic vacuolation in glioblastoma cells. Identification of the relevant signaling pathways may uncover specific molecular targets that can be manipulated to activate non-apoptotic cell death in this type of cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:249-79. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006. PMID: 16854453
-
Proto-oncogenic H-Ras, K-Ras, and N-Ras are involved in muscle differentiation via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.Cell Res. 2010 Aug;20(8):919-34. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.92. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20603646
-
Activation of the Ral and phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase signaling pathways by the ras-related protein TC21.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;21(11):3750-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.11.3750-3762.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11340168 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of K-Ras effector organization and the role of oncogenic K-Ras in cancer initiation through G1 cell cycle deregulation.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015;12(6):669-82. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2015.1100079. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 26496174 Review.
-
Oncogenesis and the clinical significance of K-ras in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(5):2699-701. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.5.2699. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23803017 Review.
Cited by
-
Methuosis: nonapoptotic cell death associated with vacuolization of macropinosome and endosome compartments.Am J Pathol. 2014 Jun;184(6):1630-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.02.028. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24726643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Regulation of Macropinocytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6963. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136963. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SV40 Polyomavirus Activates the Ras-MAPK Signaling Pathway for Vacuolization, Cell Death, and Virus Release.Viruses. 2020 Oct 5;12(10):1128. doi: 10.3390/v12101128. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33028008 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating vacquinol-1 in rats carrying glioblastoma models RG2 and NS1.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 3;9(9):8391-8399. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23842. eCollection 2018 Feb 2. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29492202 Free PMC article.
-
Non-apoptotic cell death associated with perturbations of macropinocytosis.Front Physiol. 2015 Feb 16;6:38. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00038. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25762935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Campbell SL, Khosravi-Far R, Rossman KL, Clark GJ, Der CJ. Increasing complexity of Ras signaling. Oncogene. 1998;17:1395–1413. - PubMed
-
- Shields JM, Pruitt K, McFall A, Shaub A, Der CJ. Understanding Ras: 'it ain't over 'til it's over'. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Der CJ, Finkel T, Cooper GM. Biological and biochemical properties of human rasH genes mutated at codon 61. Cell. 1986;44:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Lowy DR, Willumsen BM. Function and regulation of Ras. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:851–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

