A triple helix within a pseudoknot is a conserved and essential element of telomerase RNA
- PMID: 17210648
- PMCID: PMC1820488
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01826-06
A triple helix within a pseudoknot is a conserved and essential element of telomerase RNA
Abstract
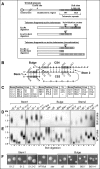
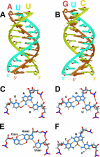
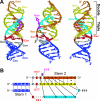
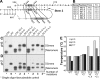
Telomerase copies a short template within its integral telomerase RNA onto eukaryotic chromosome ends, compensating for incomplete replication and degradation. Telomerase action extends the proliferative potential of cells, and thus it is implicated in cancer and aging. Nontemplate regions of telomerase RNA are also crucial for telomerase function. However, they are highly divergent in sequence among species, and their roles are largely unclear. Using in silico three-dimensional modeling, constrained by mutational analysis, we propose a three-dimensional model for a pseudoknot in telomerase RNA of the budding yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Interestingly, this structure includes a U-A.U major-groove triple helix. We confirmed the triple-helix formation in vitro using oligoribonucleotides and showed that it is essential for telomerase function in vivo. While triplex-disrupting mutations abolished telomerase function, triple compensatory mutations that formed pH-dependent G-C.C(+) triples restored the pseudoknot structure in a pH-dependent manner and partly restored telomerase function in vivo. In addition, we identified a novel type of triple helix that is formed by G-C.U triples, which also partly restored the pseudoknot structure and function. We propose that this unusual structure, so far found only in telomerase RNA, provides an essential and conserved telomerase-specific function.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The 5' arm of Kluyveromyces lactis telomerase RNA is critical for telomerase function.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(6):1875-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01683-07. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18195041 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrimidine motif triple helix in the Kluyveromyces lactis telomerase RNA pseudoknot is essential for function in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 2;110(27):10970-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309590110. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23776224 Free PMC article.
-
A critical three-way junction is conserved in budding yeast and vertebrate telomerase RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):6280-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm713. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17855392 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of telomerase RNA.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Jun;16(3):307-18. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.005. Epub 2006 May 18. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16713250 Review.
-
Telomerase is an unusual RNA-containing enzyme. A review.Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997 Nov;62(11):1206-15. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997. PMID: 9467844 Review.
Cited by
-
Structurally conserved five nucleotide bulge determines the overall topology of the core domain of human telomerase RNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 2;107(44):18761-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013269107. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20966348 Free PMC article.
-
Refined secondary-structure models of the core of yeast and human telomerase RNAs directed by SHAPE.RNA. 2015 Feb;21(2):254-61. doi: 10.1261/rna.048959.114. Epub 2014 Dec 15. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25512567 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and folding of the Tetrahymena telomerase RNA pseudoknot.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):482-495. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1153. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899638 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Interactions of Kluyveromyces lactis Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase with the Three-Way Junction and the Template Domains of Telomerase RNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 15;23(18):10757. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810757. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142669 Free PMC article.
-
TracrRNA reprogramming enables direct PAM-independent detection of RNA with diverse DNA-targeting Cas12 nucleases.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 13;15(1):5909. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50243-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39003282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ban, N., P. Nissen, J. Hansen, P. B. Moore, and T. A. Steitz. 2000. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution. Science 289:905-920. - PubMed
-
- Cech, T. R. 2004. Beginning to understand the end of the chromosome. Cell 116:273-279. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. L., M. A. Blasco, and C. W. Greider. 2000. Secondary structure of vertebrate telomerase RNA. Cell 100:503-514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
