Phosphorylated acidic serine-aspartate-rich MEPE-associated motif peptide from matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein inhibits phosphate regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X-chromosome enzyme activity
- PMID: 17210763
- PMCID: PMC3357085
- DOI: 10.1677/joe.1.07059
Phosphorylated acidic serine-aspartate-rich MEPE-associated motif peptide from matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein inhibits phosphate regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X-chromosome enzyme activity
Abstract
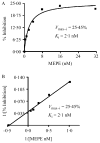
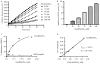
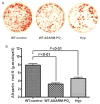
Inactivating PHEX (phosphate regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X chromosome) mutations cause X-linked hypophosphatemia in humans and mice (Hyp) through overproduction of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) a phosphaturic factor, by osteocytes. Matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) is also elevated in Hyp and other hypophosphatemic disorders. In addition, the administration of an ASARM (acidic serine-aspartate rich MEPE-associated motif) peptide derived from MEPE causes phosphaturia and inhibits bone mineralization in mice, suggesting that MEPE also plays a role in phosphate homeostasis. Since recent studies found that MEPE binds specifically to PHEX in vitro, we tested the effect of recombinant-MEPE and its ASARM peptide on PHEX enzyme activity in vitro and FGF23 expression in bone marrow stromal cell cultures ex vivo. We found that both recombinant MEPE and synthetic phosphorylated ASARM peptide (ASARM-PO(4)) inhibit PHEX enzyme activities in an in vitro fluorescent-quenched PHEX enzyme activity assay. The ASARM-PO(4) peptide inhibits PHEX enzyme activity in a dose-dependent manner with a K(i) of 128 nM and V(max-i) of 100%. Recombinant MEPE also inhibits PHEX activity (K(i) = 2 nM and V(max-i) = 26%). Long-term bone marrow stromal cell cultures supplemented with 10 microM ASARM-PO(4) peptide resulted in significant elevation of FGF23 transcripts and inhibition of mineralization. These findings suggest that MEPE inhibits mineralization and PHEX activity and leads to increased FGF23 production. The resulting coordination of mineralization and release of a phosphaturic factor by MEPE may serve a physiological role in regulating systemic phosphate homeostasis to meet the needs for bone mineralization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Figures

References
-
- ADHR Consortium. Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nature Genetics. 2000;26:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Argiro L, Desbarats M, Glorieux FH, Ecarot B. Mepe, the gene encoding a tumor-secreted protein in oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia, is expressed in bone. Genomics. 2001;74:342–351. - PubMed
-
- Bai XY, Miao D, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC. The autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets R176Q mutation in fibroblast growth factor 23 resists proteolytic cleavage and enhances in vivo biological potency. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278:9843–9849. - PubMed
-
- Bai X, Miao D, Li J, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC. Transgenic mice overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor 23 (R176Q) delineate a putative role for parathyroid hormone in renal phosphate wasting disorders. Endocrinology. 2004;145:5269–5279. - PubMed
-
- Benet-Pages A, Lorenz-Depiereux B, Zischka H, White KE, Econs MJ, Strom TM. FGF23 is processed by proprotein convertases but not by PHEX. Bone. 2004;35:455–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

