Role for rearranged variable gene segments in directing secondary T cell receptor alpha recombination
- PMID: 17210914
- PMCID: PMC1783412
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608248104
Role for rearranged variable gene segments in directing secondary T cell receptor alpha recombination
Abstract
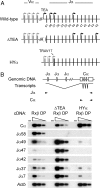
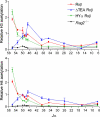
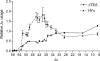
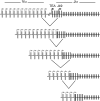
During the recombination of variable (V) and joining (J) gene segments at the T cell receptor alpha locus, a ValphaJalpha joint resulting from primary rearrangement can be replaced by subsequent rounds of secondary rearrangement that use progressively more 5' Valpha segments and progressively more 3' Jalpha segments. To understand the mechanisms that target secondary T cell receptor alpha recombination, we studied the behavior of a T cell receptor alpha allele (HYalpha) engineered to mimic a natural primary rearrangement of TRAV17 to Jalpha57. The introduced ValphaJalpha segment was shown to provide chromatin accessibility to Jalpha segments situated within several kilobases downstream and to suppress germ-line Jalpha promoter activity and accessibility at greater distances. As a consequence, the ValphaJalpha segment directed secondary recombination events to a subset of Jalpha segments immediately downstream from the primary rearrangement. The data provide the mechanistic basis for a model of primary and secondary T cell receptor alpha recombination in which recombination events progress in multiple small steps down the Jalpha array.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tcrd Rearrangement Redirects a Processive Tcra Recombination Program to Expand the Tcra Repertoire.Cell Rep. 2017 Jun 6;19(10):2157-2173. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.045. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28591585 Free PMC article.
-
The tight interallelic positional coincidence that distinguishes T-cell receptor Jalpha usage does not result from homologous chromosomal pairing during ValphaJalpha rearrangement.EMBO J. 2001 Sep 3;20(17):4717-29. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4717. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11532936 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of T cell receptor alpha gene assembly by a complex hierarchy of germline Jalpha promoters.Nat Immunol. 2005 May;6(5):481-9. doi: 10.1038/ni1189. Epub 2005 Apr 3. Nat Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15806105 Free PMC article.
-
Enforcing order within a complex locus: current perspectives on the control of V(D)J recombination at the murine T-cell receptor alpha/delta locus.Immunol Rev. 2004 Aug;200:224-32. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00155.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15242408 Review.
-
Accessibility control of T cell receptor gene rearrangement in developing thymocytes. The TCR alpha/delta locus.Immunol Res. 2000;22(2-3):127-35. doi: 10.1385/IR:22:2-3:127. Immunol Res. 2000. PMID: 11339350 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods for Study of Mouse T Cell Receptor α and β Gene Rearrangements.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2580:261-282. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2740-2_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36374463
-
Tcrd Rearrangement Redirects a Processive Tcra Recombination Program to Expand the Tcra Repertoire.Cell Rep. 2017 Jun 6;19(10):2157-2173. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.045. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28591585 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical modelling of the V-J combinations of the T cell receptor TRA/TRD locus.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Feb 19;6(2):e1000682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000682. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20174554 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Ex Vivo Culture of Vδ1+CD4+γδ T Cells, an Extrathymic αβT-cell Progenitor.J Vis Exp. 2015 Dec 7;(106):e53482. doi: 10.3791/53482. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26709831 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA damage- and transcription-associated protein paxip1 controls thymocyte development and emigration.Immunity. 2012 Dec 14;37(6):971-85. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 23159437 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

