Increase in weight induced by muraglitazar, a dual PPARalpha/gamma agonist, in db/db mice: adipogenesis/or oedema?
- PMID: 17211457
- PMCID: PMC2189717
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707000
Increase in weight induced by muraglitazar, a dual PPARalpha/gamma agonist, in db/db mice: adipogenesis/or oedema?
Abstract
Background and purpose: Muraglitazar, a dual PPARalpha/gamma agonist, caused a robust increase in body weight in db/db mice. The purpose of the study was to see if this increase in weight was due to oedema and/or adipogenesis.
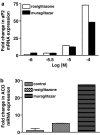
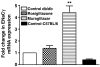
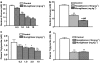
Experimental approach: The affinity of muraglitazar at PPARalpha/gamma receptors was characterized using transactivation assays. Pre-adipocyte differentiation, expression of genes for adipogenesis (aP2), fatty acid oxidation (ACO) and sodium reabsorption (ENaCgamma and Na+, K+-ATPase); haemodilution parameters and serum electrolytes were measured to delineate the role of muraglitazar in causing weight gain vis a vis rosiglitazone.
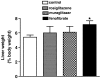
Key results: Treatment with muraglitazar (10 mg kg(-1)) for 14 days significantly reduced plasma glucose and triglycerides. Reduction in plasma glucose was significantly greater than after similar treatment with rosiglitazone (10 mg kg(-1)). A marked increase in weight was also observed with muraglitazar that was significantly greater than with rosiglitazone. Muraglitazar increased aP2 mRNA and caused adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells similar to rosiglitazone. It also caused a marked increase in ACO mRNA in the liver of the treated mice. Expression of mRNA for ENaCgamma and Na+, K+-ATPase in kidneys was up-regulated after either treatment. Increased serum electrolytes and decreased RBC count, haemoglobin and haematocrit were observed with both muraglitazar and rosiglitazone.
Conclusions and implications: Although muraglitazar has a better glucose lowering profile, it also has a greater potential for weight gain than rosiglitazone. In conclusion, muraglitazar causes both robust adipogenesis and oedema in a 14-day treatment of db/db mice as observed in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Muraglitazar, a novel dual (alpha/gamma) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor activator, improves diabetes and other metabolic abnormalities and preserves beta-cell function in db/db mice.Diabetes. 2006 Jan;55(1):240-8. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16380499
-
Combination of dipeptidylpeptidase IV inhibitor and low dose thiazolidinedione: preclinical efficacy and safety in db/db mice.Life Sci. 2007 Jun 13;81(1):72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.04.026. Epub 2007 May 1. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17532347
-
Anti-diabetic effect of amorphastilbol through PPARα/γ dual activation in db/db mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Mar 1;432(1):73-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.083. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23376064
-
Muraglitazar (Bristol-Myers Squibb/Merck).Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005 Apr;6(4):427-34. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15898350 Review.
-
Muraglitazar and the FDA: what constitutes drug safety?Prev Cardiol. 2006 Spring;9(2):110-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1520-037x.2000.5474.x. Prev Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16603830 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
PPAR Agonists and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes.PPAR Res. 2008;2008:245410. doi: 10.1155/2008/245410. PPAR Res. 2008. PMID: 18288280 Free PMC article.
-
MD001, a Novel Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor α/γ Agonist, Improves Glucose and Lipid Metabolism.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 7;9(1):1656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38281-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30733541 Free PMC article.
-
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in cardiovascular diseases: experimental benefits and clinical challenges.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;172(23):5512-22. doi: 10.1111/bph.13029. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25438608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as targets to treat metabolic diseases: Focus on the adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul 14;29(26):4136-4155. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i26.4136. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37475842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal and vascular mechanisms of thiazolidinedione-induced fluid retention.PPAR Res. 2008;2008:943614. doi: 10.1155/2008/943614. PPAR Res. 2008. PMID: 18784848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astra-Zeneca Press release AstraZeneca discontinues development of GALIDA TM (tesaglitazar) May 6, 2006.
-
- Barlocco D. Muraglitazar. Curr Opin Invest Drugs. 2005;6:427–434. - PubMed
-
- Belder R.FDA advisory committee transcript on muraglitazar 200564Available at
-
- Bernlohr DA, Bolanowski MA, Kelly TJJ, Lane MD. Evidence for an increase in transcription of specific mRNAs during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:5563–5567. - PubMed
-
- Bristol-Meyer Squibb Company News BMY announces discontinuation of development of muraglitazar, an investigational oral treatment for Type 2 Diabetes. May 18, 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

