Potentiation of antitumour activity of docetaxel by combination with trastuzumab in a human prostate cancer xenograft model and underlying mechanisms
- PMID: 17211467
- PMCID: PMC2359985
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603553
Potentiation of antitumour activity of docetaxel by combination with trastuzumab in a human prostate cancer xenograft model and underlying mechanisms
Abstract
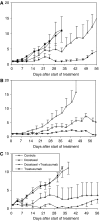
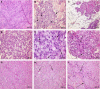
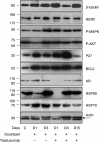
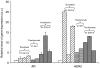
Antitumour activity of docetaxel (Taxotere) in hormone-dependent (HD) and hormone-independent (HID) prostate cancer PAC120 xenograft model was previously reported, and its level was associated with HER2 protein expression. In the present study, we evaluate the antitumour effects of docetaxel combined with trastuzumab (Herceptin), an anti-HER2 antibody. Although trastuzumab alone had no effect on tumour growth, it potentiated the antitumour activity of docetaxel in HD tumours and more strongly in HID variants. Using the HID28 variant, we show that docetaxel treatment of tumour-bearing mice induces an increased HER2 mRNA expression of the tyrosine kinase receptor of 25-fold 24 h after docetaxel treatment, while HER2 protein and p-AKT decreased. This was followed by an increase of HER2 protein 3 days (two-fold) after docetaxel treatment and by a strong HER2 release in the serum of treated mice; expression of phospho-ERK, p27, BCL2 and HSP70 concomitantly increased. Similar molecular alterations were induced by docetaxel plus trastuzumab combination, except for that there was a transient and complete disappearance of AR and HSP90 proteins 24 h after treatment. We show that in addition to its known effects on tubulin and mitotic spindles, docetaxel induces complex signalisation pathway mechanisms in surviving cells, including HER2, which can be pharmacologically targeted. This study suggests that the docetaxel/trastuzumab combination may prove an effective therapeutic approach for HER2-expressing hormone-refractory prostate cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Abal M, Andreu JM, Barasoain I (2003) Taxanes: microtubule and centrosome targets, and cell cycle dependent mechanisms of action. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 3: 193–203 - PubMed
-
- Agus DB, Scher HI, Higgins B, Fox WD, Heller G, Fazzari M, Cordon-Cardo C, Golde DW (1999) Response of prostate cancer to anti-Her-2/neu antibody in androgen-dependent and -independent human xenograft models. Cancer Res 59: 4761–4764 - PubMed
-
- Burns RG, Islam K, Chapman R (1984) The multiple phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein MAP2 controls the MAP2:tubulin interaction. Eur J Biochem 141: 609–615 - PubMed
-
- Calvo BF, Levine AM, Marcos M, Collins QF, Iacocca MV, Caskey LS, Gregory CW, Lin Y, Whang YE, Earp HS, Mohler JL (2003) Human epidermal receptor-2 expression in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9: 1087–1097 - PubMed
-
- Craft N, Shostak Y, Carey M, Sawyers CL (1999) A mechanism for hormone-independent prostate cancer through modulation of androgen receptor signaling by the HER-2/neu tyrosine kinase. Nat Med 5: 280–285 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

