Single eye analysis and contralateral eye comparison of tear proteins in normal and dry eye model rabbits by MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry using wax-coated target plates
- PMID: 17211596
- PMCID: PMC2268083
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-006-1018-9
Single eye analysis and contralateral eye comparison of tear proteins in normal and dry eye model rabbits by MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry using wax-coated target plates
Abstract
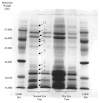
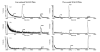
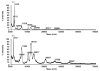
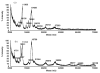
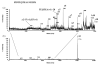
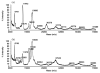
A study of rabbit tear protein expression in a dry eye rabbit model was performed to determine if a pattern in expressed proteins could be identified. The uniqueness of the model allows the comparison of normal (control) eye tear protein expression with surgically induced dry eye tear protein expression in individual animals. The sensitivity of the method allows for single eye analysis. One-dimensional mini-gel electrophoresis of the tear proteins did not show substantial differences between band patterns of the normal versus the dry eye, but was used to assess the molecular weight ranges of the major proteins. Specific assignments of some of the predominant proteins were obtained by tandem mass spectrometry (MS) which showed that the lower molecular weight lipid-binding proteins (approximately 10 kDa to 36 kDa) constitute a considerable amount of the observed protein, followed in lesser quantities by the transferrins which have higher molecular weights ranging from 70 kDa to 85 kDa. Enhancement of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-ToF) MS linear mode analysis of intact proteins in tear fluid was demonstrated through the use of wax-coated MALDI plates and spot washing. MALDI-ToF MS analysis of the expressed tear proteins illustrates that differences between normal eye tear and dry eye tear protein content are manifested in changes in the lower molecular weight lipid-binding proteins such as lipophilin which exhibits an increase in concentration in the dry eye, and beta-2 microglobulin which undergoes a decrease.
Figures

References
-
- Holly FJ, Lemp MA. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1973;13:29. - PubMed
-
- Ellison SA, Jacobson M, Levine MJ. Lacrimal and salivary proteins. Immunol eye, workshop 3: immunological aspects of ocular disease: infection, inflammation, and allergy; 1980; 1981. Meeting Date.
-
- Frey WH, DeSota-Johnson D, Hoffman C, McCall JT. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981;92:559. - PubMed
-
- Holly FJ, Hong BS. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1982;59:43. - PubMed
-
- Gachon AM, Richard J, Dastugue B. Curr Eye Res. 1982;2:301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

