Ophthalmic manifestations and histopathology of infantile nephropathic cystinosis: report of a case and review of the literature
- PMID: 17212992
- PMCID: PMC1850966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2006.10.006
Ophthalmic manifestations and histopathology of infantile nephropathic cystinosis: report of a case and review of the literature
Abstract
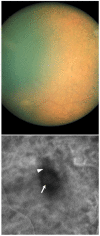
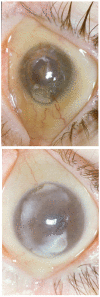
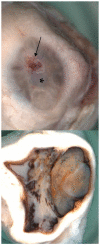
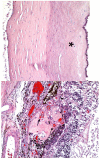
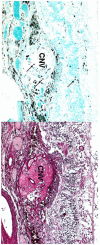
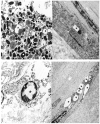
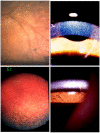
Cystinosis is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by the intracellular accumulation of cystine, the disulfide of the amino acid cysteine, in many organs and tissues. Infantile nephropathic cystinosis is the most severe phenotype. Corneal crystal accumulation and pigmentary retinopathy were originally the most commonly described ophthalmic manifestations, but successful kidney transplantation significantly changed the natural history of the disease. As cystinosis patients now live longer, long-term complications in extrarenal tissues, including the eye, have become apparent. A case of an adult patient with infantile nephropathic cystinosis is reported. He presented with many long-term ocular complications of cystinosis. After 4 years of follow-up, the patient died from sepsis. Pathology of the phthisical eyes demonstrated numerous electron-transparent polygonal spaces, bounded by single membrane, in corneal cells, retinal pigment epithelial cells, and even choroidal endothelial cells. The ophthalmic manifestations and pathology of infantile nephropathic cystinosis are discussed and reviewed in light of the current report and other cases in the literature.
Figures

References
-
- ___ Feature photo. Cystinosis with extensive choroidal involvement. Arch Ophthalmol. 1965;74:868–9. - PubMed
-
- Aberhalden E. Familiare cystidiathesis. ZtschrPhysiol Chem. 1903;38:557.
-
- Almond PS, Matas AJ, Nakhleh RE, et al. Renal transplantation for infantile cystinosis: long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Surg. 1993;28:232–8. - PubMed
-
- Anikster Y, Lucero C, Guo J, et al. Ocular nonnephropathic cystinosis: clinical, biochemical, and molecular correlations. Pediatr Res. 2000;47:17–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

