Specificity of the deoxyhypusine hydroxylase-eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF5A) interaction: identification of amino acid residues of the enzyme required for binding of its substrate, deoxyhypusine-containing eIF5A
- PMID: 17213197
- PMCID: PMC1852541
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M607495200
Specificity of the deoxyhypusine hydroxylase-eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF5A) interaction: identification of amino acid residues of the enzyme required for binding of its substrate, deoxyhypusine-containing eIF5A
Abstract
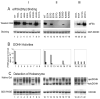
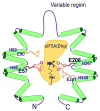
Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH) is a novel metalloenzyme that catalyzes the final step of the post-translational synthesis of hypusine (Nepsilon-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)lysine) in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A). Hypusine synthesis is unique in that it occurs in only one protein, denoting the strict specificity of the modification enzymes toward the substrate protein. The specificity of the interaction between eIF5A and DOHH was investigated using human eIF5A (eIF5A-1 isoform) and human recombinant DOHH. DOHH displayed a strong preference for binding the deoxyhypusine-containing form of eIF5A, over the eIF5A precursor or the hypusine-containing eIF5A, indicating a role for the deoxyhypusine residue in binding. In addition to the deoxyhypusine residue, a large portion of the eIF5A polypeptide (>20-90 amino acids) is required for effective modification by DOHH. We have identified the amino acid residues of DOHH that are critical for substrate binding by alanine substitution of 36 conserved amino acid residues. Of these, alanine substitution at Glu57, Glu90, Glu208, Glu241, Gly63, or Gly214 caused a severe impairment in eIF5A(Dhp) binding, with a complete loss of binding and activity in the E57A and E208A mutant enzymes. Only aspartate substitution mutants, E57D or E208D, retained partial activity and substrate binding, whereas alanine, glutamine, or asparagine mutants did not. These findings support a proposed model of DOHH-eIF5A binding in which the amino group(s) of the deoxyhypusine side chain of the substrate is primarily anchored by gamma-carboxyl groups of Glu57 and Glu208 at the DOHH active site.
Figures


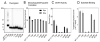
Similar articles
-
A unique modification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A shows the presence of the complete hypusine pathway in Leishmania donovani.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033138. Epub 2012 Mar 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22438895 Free PMC article.
-
The post-translational synthesis of a polyamine-derived amino acid, hypusine, in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A).J Biochem. 2006 Feb;139(2):161-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvj034. J Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16452303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular cloning, expression, and structural prediction of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase: a HEAT-repeat-containing metalloenzyme.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 3;103(1):51-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509348102. Epub 2005 Dec 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16371467 Free PMC article.
-
Production of active recombinant eIF5A: reconstitution in E.coli of eukaryotic hypusine modification of eIF5A by its coexpression with modifying enzymes.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2011 Mar;24(3):301-9. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzq110. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2011. PMID: 21131325 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational synthesis of hypusine: evolutionary progression and specificity of the hypusine modification.Amino Acids. 2007 Aug;33(2):341-50. doi: 10.1007/s00726-007-0525-0. Epub 2007 May 4. Amino Acids. 2007. PMID: 17476569 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Molecular and Physiological Effects of Protein-Derived Polyamines in the Intestine.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 11;12(1):197. doi: 10.3390/nu12010197. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31940783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent insights into eukaryotic translation initiation factors 5A1 and 5A2 and their roles in human health and disease.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Apr 29;20:142. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01226-7. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32368188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assay of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase activity.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;720:207-16. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-034-8_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21318876 Free PMC article.
-
The hypusine-containing translation factor eIF5A.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Sep-Oct;49(5):413-25. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2014.939608. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25029904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypusine, a polyamine-derived amino acid critical for eukaryotic translation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 30;293(48):18710-18718. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.003341. Epub 2018 Sep 26. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30257869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

