Weight estimation in resuscitation: is the current formula still valid?
- PMID: 17213259
- PMCID: PMC2083737
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2006.107284
Weight estimation in resuscitation: is the current formula still valid?
Erratum in
- Arch Dis Child. 2007 Jul;92(7):657
Abstract
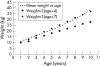
Objectives: To gather data on the ages and weights of paediatric patients between 1 and 10 years of age, and to compare these data with the current weight estimation formula weight(kg) = 2(age+4). If a significant difference was found, the data would be used to derive a more accurate formula.
Design: Retrospective study using data collected from paediatric attendances at an emergency department (ED).
Setting: A large ED in a major UK city, treating both children and adults.
Patients: 17 244 children aged 1-10 years, attending the ED between June and December 2005.
Main outcome measures: Weight difference between the measured weight and the expected weight, the latter given by weight = 2(age+4).
Results: The weights of seriously ill children were recorded in only 41.5% of cases, necessitating a weight estimate in the remainder. The formula weight = 2(age+4) underestimated children's weights by a mean of 18.8% (95% confidence interval (95% CI) 18.42% to 19.18%). Using linear regression and analysis of each individual age group, ten new formulas were tested. Of these formulas, weight(kg) = 3(age)+7 proved the most accurate with a mean underestimate of just 2.48% (95% CI 2.17% to 2.79%).
Conclusions: Weight estimation remains of paramount importance in paediatric resuscitation. This study shows that the current estimation formula provides a significant underestimate of children's weights. When used to calculate drug and fluid dosages, this may lead to the under-resuscitation of a critically ill child. The formula weight(kg) = 3(age)+7 provided a safe and more accurate estimate of the weight of today's child.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Comment in
-
Underestimation potentially better than overestimation.Arch Dis Child. 2007 Oct;92(10):937. Arch Dis Child. 2007. PMID: 17895346 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Estimating children's weights: a developing country perspective.Arch Dis Child. 2007 Oct;92(10):938-9. Arch Dis Child. 2007. PMID: 17895348 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Advanced Life Support Group Advanced paediatric life support. 3rd edn. London: BMJ Publishing Group, 2003
-
- Luscombe M D, “Kids aren't like what they used to be”: a study of paediatric patient's weights and their relationship to current weight estimation formulae Br J Anaesth. 2005;95 (4):578.
-
- Kimm S Y S, Obarzanek E. Childhood obesity: a new pandemic of the new millennium. Pediatrics 2002111(5)1003–1007. - PubMed
-
- Tackling child obesity – first steps. Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General prepared jointly by the Audit Commission, the Healthcare Commission and the National Audit Office. HC 801 2005–2006. London: Stationery Office, 2006
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical