Distinguishing diabetic nephropathy from other causes of glomerulosclerosis: an update
- PMID: 17213346
- PMCID: PMC1860608
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2005.035592
Distinguishing diabetic nephropathy from other causes of glomerulosclerosis: an update
Abstract
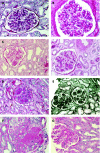
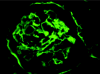
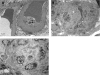
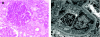
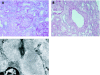
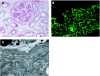
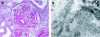
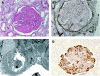
Diabetic nephropathy is a common cause of end-stage renal disease worldwide. It is characterised by diffuse or nodular glomerulosclerosis, afferent and efferent hyaline arteriolosclerosis, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis and atrophy. Diffuse and nodular diabetic glomerulosclerosis share similar histological features with other clinical conditions. Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy studies, and clinicopathological correlation are essential to differentiate diabetic nephropathy from other conditions that result in diffuse and nodular glomerulosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Essential mixed cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Light, immunofluorescence, and ultrastructural study of two cases.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Nov;109(11):1036-9. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985. PMID: 3840355
-
A case of idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis mimicking diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson type).Pathol Res Pract. 2002;198(5):375-9. doi: 10.1078/0344-0338-00269. Pathol Res Pract. 2002. PMID: 12092775
-
Renal morphologic lesions reminiscent of diabetic nephropathy.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013 Mar;137(3):351-9. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0243-RA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23451746 Review.
-
"Diabetic nephropathy" in a non-diabetic patient.Pathol Res Pract. 2016 Dec;212(12):1199-1201. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2016.09.018. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27688084
-
Ultrastructural characteristics of diabetic nephropathy.Med Electron Microsc. 2000;33(2):65-73. doi: 10.1007/s007950070004. Med Electron Microsc. 2000. PMID: 11810461 Review.
Cited by
-
FcER1: A Novel Molecule Implicated in the Progression of Human Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 1;12:769972. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.769972. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925339 Free PMC article.
-
Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging of Renal Vascular Alterations in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats during the Development of Diabetic Kidney Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;13(20):3197. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203197. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892017 Free PMC article.
-
From fibrosis to sclerosis: mechanisms of glomerulosclerosis in diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes. 2008 Jun;57(6):1439-45. doi: 10.2337/db08-0061. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18511444 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Cardiovascular health metrics and diabetic nephropathy: a nationally representative cross-sectional study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Nov;56(11):3569-3584. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04097-3. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38839692
-
Artificial intelligence assists identification and pathologic classification of glomerular lesions in patients with diabetic nephropathy.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 29;22(1):397. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05221-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38684996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Estacio R O, Schrier R W. Diabetic nephropathy: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prevention of progression. Adv Int Med 200146359–408. - PubMed
-
- Parving H H. Diabetic nephropathy: prevention and treatment. Kidney Int 2001602041–2055. - PubMed
-
- Hostetter T H. Hyperfiltration and glomerulosclerosis. Semin Nephrol 200323194–199. - PubMed
-
- Wolf G, Butzmann U, Wenzel U O. The renin‐angiotensin system and progression of renal disease: from hemodynamics to cell biology. Nephron Physiol 2003933–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical