Analysis of a study of the users, uses, and future agenda of the UMLS
- PMID: 17213497
- PMCID: PMC2213464
- DOI: 10.1197/jamia.M2202
Analysis of a study of the users, uses, and future agenda of the UMLS
Abstract
Objectives: The UMLS constitutes the largest existing collection of medical terms. However, little has been published about the users and uses of the UMLS. This study sheds light on these issues.
Design: We designed a questionnaire consisting of 26 questions and distributed it to the UMLS user mailing list. Participants were assured complete confidentiality of their replies. To further encourage list members to respond, we promised to provide them with early results prior to publication. Sector analysis of the responses, according to employment organizations is used to obtain insights into some responses.
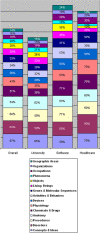
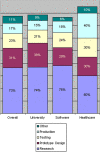
Results: We received 70 responses. The study confirms two intended uses of the UMLS: access to source terminologies (75%), and mapping among them (44%). However, most access is just to a few sources, led by SNOMED, MeSH, and ICD. Out of 119 reported purposes of use, terminology research (37), information retrieval (19), and terminology translation (14) lead. Four important observations are that the UMLS is widely used as a terminology (77%), even though it was not designed as one; many users (73%) want the NLM to mark concepts with multiple parents in an indented hierarchy and to derive a terminology from the UMLS (73%). Finally, auditing the UMLS is a top budget priority (35%) for users.
Conclusions: The study reports many uses of the UMLS in a variety of subjects from terminology research to decision support and phenotyping. The study confirms that the UMLS is used to access its source terminologies and to map among them. Two primary concerns of the existing user base are auditing the UMLS and the design of a UMLS-based derived terminology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Who is using the UMLS and how - insights from the UMLS user annual reports.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2006;2006:274-8. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2006. PMID: 17238346 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II evaluation of clinical coding schemes: completeness, taxonomy, mapping, definitions, and clarity. CPRI Work Group on Codes and Structures.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1997 May-Jun;4(3):238-51. doi: 10.1136/jamia.1997.0040238. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1997. PMID: 9147343 Free PMC article.
-
A tool for sharing annotated research data: the "Category 0" UMLS (Unified Medical Language System) vocabularies.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2003 Jun 16;3:6. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-3-6. Epub 2003 Jun 16. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2003. PMID: 12809560 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping scientific landscapes in UMLS research: a scientometric review.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020 Oct 1;27(10):1612-1624. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa107. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33059367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Unified Medical Language System at 30 Years and How It Is Used and Published: Systematic Review and Content Analysis.JMIR Med Inform. 2021 Aug 27;9(8):e20675. doi: 10.2196/20675. JMIR Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 34236337 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A survey of SNOMED CT direct users, 2010: impressions and preferences regarding content and quality.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2011 Dec;18 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i36-44. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000341. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2011. PMID: 21836159 Free PMC article.
-
The Neighborhood Auditing Tool: a hybrid interface for auditing the UMLS.J Biomed Inform. 2009 Jun;42(3):468-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2009.01.006. J Biomed Inform. 2009. PMID: 19475725 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming an obstacle in expanding a UMLS semantic type extent.J Biomed Inform. 2012 Feb;45(1):61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2011.08.021. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Biomed Inform. 2012. PMID: 21925287 Free PMC article.
-
A study of terminology auditors' performance for UMLS semantic type assignments.J Biomed Inform. 2012 Dec;45(6):1042-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 Jun 9. J Biomed Inform. 2012. PMID: 22687822 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling multi-typed structurally viewed chemicals with the UMLS Refined Semantic Network.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2009 Jan-Feb;16(1):116-31. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2604. Epub 2008 Oct 24. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2009. PMID: 18952946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UMLS User Mailing List. Available at: umls-users@umlsinfo.nlm.nih.gov (it was changed to UMLSUSERS-L@list.nih.gov on September 1, 2005).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

