Novel host response therapeutic approaches to treat periodontal diseases
- PMID: 17214846
- PMCID: PMC2570321
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2006.00166.x
Novel host response therapeutic approaches to treat periodontal diseases
Figures
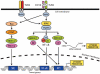
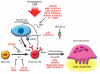
References
-
- Adams JL, Badger AM, Kumar S, Lee JC. p38 MAP kinase: molecular target for the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Prog Med Chem. 2001;38:1–60. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Hemmi H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett. 2003;85:85–95. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Sato S. Toll-like receptors and their signaling mechanisms. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35:555–562. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shammari KF, Giannobile WV, Aldredge WA, Iacono VJ, Eber RM, Wang HL, Oringer RJ. Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on C-telopeptide pyridinoline cross-links (ICTP) and interleukin-1 levels. J Periodontol. 2001;72:1045–1051. - PubMed
-
- Ambili R, Santhi WS, Janam P, Nandakumar K, Pillai MR. Expression of activated transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB in periodontally diseased tissues. J Periodontol. 2005;76:1148–1153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

