Bone morphogenetic protein 2 activates Smad6 gene transcription through bone-specific transcription factor Runx2
- PMID: 17215250
- PMCID: PMC2636961
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M610997200
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 activates Smad6 gene transcription through bone-specific transcription factor Runx2
Abstract
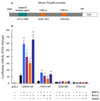
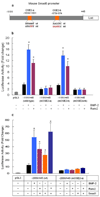
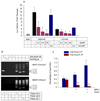
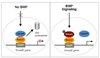
BMP-2 plays an essential role in osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation, but its signaling mechanism has not been fully defined. In the present studies, we investigated the mechanism through which BMP-2 activates the Smad6 gene. A -2006/+45 Smad6 promoter-luciferase construct was generated along with deletions and Runx2 binding site mutations to examine the role of Smad1 and Runx2 signaling following BMP-2 stimulation in osteoblasts. Transfection of Runx2 or treatment with BMP-2-stimulated promoter activity of the -2006/+45 and -1191/+45 reporters but not the -829/+45 and -374/+45 reporters. No Smad1/5 binding site is present in the -1191/-829 region of the Smad6 promoter. Mutation of the OSE2-a site (-1036/-1031) completely abolished the stimulatory effect of Runx2 as well as BMP-2 on the -2006/+45 and -1191/+45 Smad6 reporters. Gel shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays showed that Runx2 binds the OSE2-a element. ChIP assays demonstrated that Smad1 also interacts with the OSE2-a site at the Smad6 promoter through Runx2. The protein degradation of Runx2 is mediated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1. In the present studies, we found that Smurf1 binds the OSE2-a site through Runx2 and inhibits Smad6 gene transcription. Treatment with BMP-2 and transfection of Smad1 abolished Smurf1 binding to the OSE2 site. These results show that Smad1 binding excludes Smurf1 interaction with the OSE2 site and promotes Smad6 gene transcription.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Smad6 interacts with Runx2 and mediates Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-induced Runx2 degradation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Feb 10;281(6):3569-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506761200. Epub 2005 Nov 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16299379 Free PMC article.
-
Murine and chicken chondrocytes regulate osteoclastogenesis by producing RANKL in response to BMP2.J Bone Miner Res. 2008 Mar;23(3):314-25. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.071025. J Bone Miner Res. 2008. PMID: 17967138 Free PMC article.
-
Menin is required for bone morphogenetic protein 2- and transforming growth factor beta-regulated osteoblastic differentiation through interaction with Smads and Runx2.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 24;279(39):40267-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401312200. Epub 2004 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15150273
-
Smad-Runx interactions during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S15-22. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263661 Review.
-
Integration of BMP, Wnt, and notch signaling pathways in osteoblast differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Dec;112(12):3491-501. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23287. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21793042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncostatin M promotes bone formation independently of resorption when signaling through leukemia inhibitory factor receptor in mice.J Clin Invest. 2010 Feb;120(2):582-92. doi: 10.1172/JCI40568. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20051625 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts.Biofactors. 2010 Jan-Feb;36(1):25-32. doi: 10.1002/biof.72. Biofactors. 2010. PMID: 20087883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles and regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β and BMP signaling in bone and cartilage development, homeostasis and disease.Cell Res. 2024 Feb;34(2):101-123. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00918-9. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38267638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smurf control in bone cells.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Jun 1;110(3):554-63. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22586. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20512916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced signaling and osteogenesis is regulated by cell shape, RhoA/ROCK, and cytoskeletal tension.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 May 1;21(7):1176-86. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0293. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 21967638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishida W, Hamamoto T, Kusanagi K, Yagi K, Kawabata M, Takehara K, Sampath TK, Kato M, Miyazono K. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:6075–6079. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH. Cell. 1998;95:737–740. (Review) - PubMed
-
- Hanai J, Chen LF, Kanno T, Ohtani-Fujita N, Kim WY, Guo WH, Imamura T, Ishidou Y, Fukuchi M, Shi MJ, Stavnezer J, Kawabata M, Miyazono K, Ito Y. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:31577–31582. - PubMed
-
- Zhao M, Qiao M, Oyajobi BO, Mundy GR, Chen D. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:27939–27944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

