A WAVE-1 and WRP signaling complex regulates spine density, synaptic plasticity, and memory
- PMID: 17215396
- PMCID: PMC3740594
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3209-06.2006
A WAVE-1 and WRP signaling complex regulates spine density, synaptic plasticity, and memory
Abstract
The scaffolding protein WAVE-1 (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein family member 1) directs signals from the GTPase Rac through the Arp2/3 complex to facilitate neuronal actin remodeling. The WAVE-associated GTPase activating protein called WRP is implicated in human mental retardation, and WAVE-1 knock-out mice have altered behavior. Neuronal time-lapse imaging, behavioral analyses, and electrophysiological recordings from genetically modified mice were used to show that WAVE-1 signaling complexes control aspects of neuronal morphogenesis and synaptic plasticity. Gene targeting experiments in mice demonstrate that WRP anchoring to WAVE-1 is a homeostatic mechanism that contributes to neuronal development and the fidelity of synaptic connectivity. This implies that signaling through WAVE-1 complexes is essential for neural plasticity and cognitive behavior.
Figures
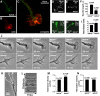

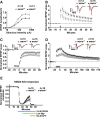
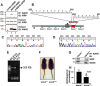

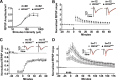

References
-
- Allen KM, Gleeson JG, Bagrodia S, Partington MW, MacMillan JC, Cerione RA, Mulley JC, Walsh CA. PAK3 mutation in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet. 1998;20:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Angeloni D, Lindor NM, Pack S, Latif F, Wei MH, Lerman MI. CALL gene is haploinsufficient in a 3p- syndrome patient. Am J Med Genet. 1999;86:482–485. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA. Culturing nerve cells. Ed 2. Cambridge, MA: MIT; 1998.
-
- Bear JE, Loureiro JJ, Libova I, Fassler R, Wehland J, Gertler FB. Negative regulation of fibroblast motility by Ena/VASP proteins Cell. 2000;101:717–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
