Cholinergic interneurons control the excitatory input to the striatum
- PMID: 17215400
- PMCID: PMC6672079
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3709-06.2007
Cholinergic interneurons control the excitatory input to the striatum
Abstract
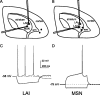
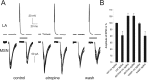
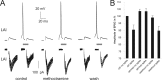
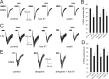
How the extent and time course of presynaptic inhibition depend on the action potentials of the neuron controlling the terminals is unknown. We investigated this issue in the striatum using paired recordings from cholinergic interneurons and projection neurons. Glutamatergic EPSCs were evoked in projection neurons and cholinergic interneurons by stimulation of afferent fibers in the cortex and the striatum, respectively. A single spike in a cholinergic interneuron caused significant depression of the evoked glutamatergic EPSC in 34% of projection neurons located within 100 microm and 41% of cholinergic interneurons located within 200 microm. The time course of these effects was similar in the two cases, with EPSC inhibition peaking 20-30 ms after the spike and disappearing after 40-80 ms. Maximal depression of EPSC amplitude was up to 27% in projection neurons and to 19% in cholinergic interneurons. These effects were reversibly blocked by muscarinic receptor antagonists (atropine or methoctramine), which also significantly increased baseline EPSC (evoked without a preceding spike in the cholinergic interneuron), suggesting that some tonic cholinergic presynaptic inhibition was present. This was confirmed by the fact that lowering extracellular potassium, which silenced spontaneously active cholinergic interneurons, also increased baseline EPSC amplitude, and these effects were occluded by previous application of muscarinic receptor antagonists. Collectively, these results show that a single spike in a cholinergic interneuron exerts a fast and powerful inhibitory control over the glutamatergic input to striatal neurons.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tonic enhancement of endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde suppression of inhibition by cholinergic interneuron activity in the striatum.J Neurosci. 2007 Jan 17;27(3):496-506. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4644-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17234582 Free PMC article.
-
Neostriatal GABAergic Interneurons Mediate Cholinergic Inhibition of Spiny Projection Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Sep 7;36(36):9505-11. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0466-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27605623 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of an afterhyperpolarization by the substantia nigra induces pauses in the tonic firing of striatal cholinergic interneurons.J Neurosci. 2004 Nov 3;24(44):9870-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3225-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15525771 Free PMC article.
-
Spike-timing dependent plasticity in striatal interneurons.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Apr;60(5):780-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.023. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21262240 Review.
-
Roles of centromedian parafascicular nuclei of thalamus and cholinergic interneurons in the dorsal striatum in associative learning of environmental events.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Mar;125(3):501-513. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1713-z. Epub 2017 Mar 21. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 28324169 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Binge alcohol drinking alters the differential control of cholinergic interneurons over nucleus accumbens D1 and D2 medium spiny neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Dec 15;16:1010121. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1010121. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36589290 Free PMC article.
-
Thinking Outside the Box (and Arrow): Current Themes in Striatal Dysfunction in Movement Disorders.Neuroscientist. 2019 Aug;25(4):359-379. doi: 10.1177/1073858418807887. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Neuroscientist. 2019. PMID: 30379121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of muscarinic M1 receptor stimulation on reinforcing and neurochemical effects of cocaine in rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Nov;45(12):1994-2002. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0684-1. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32344426 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic modulation of multivesicular release regulates striatal synaptic potency and integration.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Sep;12(9):1121-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.2368. Epub 2009 Aug 9. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19668198 Free PMC article.
-
The Neurodynamics of Cognition: A Tutorial on Computational Cognitive Neuroscience.J Math Psychol. 2011 Aug 1;55(4):273-289. doi: 10.1016/j.jmp.2011.04.003. J Math Psychol. 2011. PMID: 21841845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubert I, Cecyre D, Gauthier S, Quirion R. Comparative ontogenic profile of cholinergic markers, including nicotinic and muscarinic receptors, in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1996;369:31–55. - PubMed
-
- Aznavour N, Mechawar N, Descarries L. Comparative analysis of cholinergic innervation in the dorsal hippocampus of adult mouse and rat: a quantitative immunocytochemical study. Hippocampus. 2002;12:206–217. - PubMed
-
- Barral J, Galarraga E, Bargas J. Muscarinic presynaptic inhibition of neostriatal glutamatergic afferents is mediated by Q-type Ca2+ channels. Brain Res Bull. 1999;49:285–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
