ZAP-70 kinase regulates HIV cell-to-cell spread and virological synapse formation
- PMID: 17215865
- PMCID: PMC1783460
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601509
ZAP-70 kinase regulates HIV cell-to-cell spread and virological synapse formation
Abstract
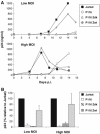
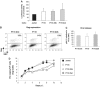
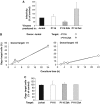
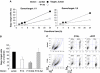
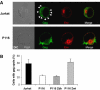
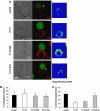
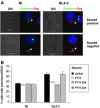
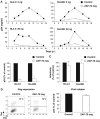
HIV efficiently spreads in lymphocytes, likely through virological synapses (VSs). These cell-cell junctions share some characteristics with immunological synapses, but cellular proteins required for their constitution remain poorly characterized. We have examined here the role of ZAP-70, a key kinase regulating T-cell activation and immunological synapse formation, in HIV replication. In lymphocytes deficient for ZAP-70, or expressing a kinase-dead mutant of the protein, HIV replication was strikingly delayed. We have characterized further this replication defect. ZAP-70 was dispensable for the early steps of viral cycle, from entry to expression of viral proteins. However, in the absence of ZAP-70, intracellular Gag localization was impaired. ZAP-70 was required in infected donor cells for efficient cell-to-cell HIV transmission to recipients and for formation of VSs. These results bring novel insights into the links that exist between T-cell activation and HIV spread, and suggest that HIV usurps components of the immunological synapse machinery to ensure its own spread through cell-to-cell contacts.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham RT, Weiss A (2004) Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 301–308 - PubMed
-
- Arpaia E, Shahar M, Dadi H, Cohen A, Roifman CM (1994) Defective T cell receptor signaling and CD8+ thymic selection in humans lacking zap-70 kinase. Cell 76: 947–958 - PubMed
-
- Barda-Saad M, Braiman A, Titerence R, Bunnell SC, Barr VA, Samelson LE (2005) Dynamic molecular interactions linking the T cell antigen receptor to the actin cytoskeleton. Nat Immunol 6: 80–89 - PubMed
-
- Barnard AL, Igakura T, Tanaka Y, Taylor GP, Bangham CR (2005) Engagement of specific T-cell surface molecules regulates cytoskeletal polarization in HTLV-1-infected lymphocytes. Blood 106: 988–995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

