Altered expression of ZO-1 and ZO-2 in Sertoli cells and loss of blood-testis barrier integrity in testicular carcinoma in situ
- PMID: 17217619
- PMCID: PMC1783719
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06559
Altered expression of ZO-1 and ZO-2 in Sertoli cells and loss of blood-testis barrier integrity in testicular carcinoma in situ
Abstract
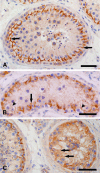
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is the noninvasive precursor of most human testicular germ cell tumors. In normal seminiferous epithelium, specialized tight junctions between Sertoli cells constitute the major component of the blood-testis barrier. Sertoli cells associated with CIS exhibit impaired maturation status, but their functional significance remains unknown. The aim was to determine whether the blood-testis barrier is morphologically and/or functionally altered. We investigated the expression and distribution pattern of the tight junction proteins zonula occludens (ZO) 1 and 2 in normal seminiferous tubules compared to tubules showing CIS. In normal tubules, ZO-1 and ZO-2 immunostaining was observed at the blood-testis barrier region of adjacent Sertoli cells. Within CIS tubules, ZO-1 and ZO-2 immunoreactivity was reduced at the blood-testis barrier region, but spread to stain the Sertoli cell cytoplasm. Western blot analysis confirmed ZO-1 and ZO-2, and their respective mRNA were shown by RT-PCR. Additionally, we assessed the functional integrity of the blood-testis barrier by lanthanum tracer study. Lanthanum permeated tight junctions in CIS tubules, indicating disruption of the blood-testis barrier. In conclusion, Sertoli cells associated with CIS show an altered distribution of ZO-1 and ZO-2 and lose their blood-testis barrier function.
Figures


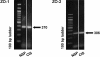



Similar articles
-
Claudin-11 is over-expressed and dislocated from the blood-testis barrier in Sertoli cells associated with testicular intraepithelial neoplasia in men.Histochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;131(6):755-64. doi: 10.1007/s00418-009-0576-2. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19241088
-
Development of Sertoli cell junctional specializations and the distribution of the tight-junction-associated protein ZO-1 in the mouse testis.Am J Anat. 1991 May;191(1):35-47. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001910104. Am J Anat. 1991. PMID: 2063808
-
Disruption of Sertoli-germ cell adhesion function in the seminiferous epithelium of the rat testis can be limited to adherens junctions without affecting the blood-testis barrier integrity: an in vivo study using an androgen suppression model.J Cell Physiol. 2005 Oct;205(1):141-57. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20377. J Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15880438
-
Molecular basis of cryptorchidism-induced infertility.Sci China Life Sci. 2010 Nov;53(11):1274-83. doi: 10.1007/s11427-010-4072-7. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Sci China Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 21046318 Review.
-
The blood-testis barrier and Sertoli cell junctions: structural considerations.Microsc Res Tech. 1992 Jan 1;20(1):3-33. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070200104. Microsc Res Tech. 1992. PMID: 1611148 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and functional characterization of a murine primary Sertoli cell line deficient of connexin43.Cell Tissue Res. 2020 Aug;381(2):309-326. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03203-y. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Cell Tissue Res. 2020. PMID: 32328805 Free PMC article.
-
Malfunction of spermatogenesis in experimental ischemic mice.J Reprod Dev. 2015;61(5):399-406. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2015-028. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Reprod Dev. 2015. PMID: 26063609 Free PMC article.
-
Human and animal fertility studies in cystinosis reveal signs of obstructive azoospermia, an altered blood-testis barrier and a subtherapeutic effect of cysteamine in testis.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 Nov;44(6):1393-1408. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12434. Epub 2021 Sep 24. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 34494673 Free PMC article.
-
Zona occludens-2 is critical for blood-testis barrier integrity and male fertility.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Oct;20(20):4268-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-12-1236. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19692573 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of rat spermatogonia and Sertoli cells reveals signaling pathways from stem cells to niche and testicular cancer cells to surrounding stroma.BMC Genomics. 2011 Jan 13;12:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-29. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21232125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dym M, Fawcett DW. The blood-testis barrier in the rat and the physiological compartmentation of the seminiferous epithelium. Biol Reprod. 1970;3:308–326. - PubMed
-
- Gondos B, Berndston WE. Postnatal and pubertal development. In: Russel LD, Griswold MD, editors. The Sertoli Cell. Clearwater, FL: Cache River Press; 1993. pp. 115–154.
-
- Steger K, Rey R, Louis F, Kliesch S, Behre HM, Nieschlag E, Hoepffner W, Bailey D, Marks A, Bergmann M. Reversion of differentiated phenotype and maturation block in Sertoli cells in pathological human testis. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:136–143. - PubMed
-
- Byers SW, Pelletier R-M. Sertoli cell tight junctions and the blood-testis barrier. In: Cerejido M, editor. Tight Junctions. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1992. pp. 279–304.
-
- Griswold MD. Interactions between germ cells and Sertoli cells in the testis. Biol Reprod. 1995;52:211–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
