Expression of cathepsin P mRNA, protein and activity in the rat choriocarcinoma cell line, Rcho-1, during giant cell transformation
- PMID: 17218008
- PMCID: PMC4159944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2006.11.007
Expression of cathepsin P mRNA, protein and activity in the rat choriocarcinoma cell line, Rcho-1, during giant cell transformation
Abstract
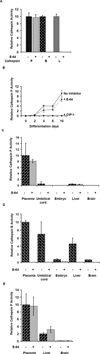
Lysosomal proteases perform critical functions in protein turnover and are essential for normal growth and development. Cathepsin P is a member of a newly discovered family of lysosomal cysteine proteases uniquely expressed in rodent placenta (PECs), and is closely related to human cathepsin L. Using the rat choriocarcinoma cell line model, Rcho-1, mRNA for the PECs cathepsins P, M, Q, R, 1, 2 was found to increase in expression during differentiation into a trophoblast giant cell phenotype. By contrast, expression of cathepsin L was not regulated. A specific enzyme assay was developed to show that activity of cathepsin P mirrored mRNA expression during differentiation. Cathepsin P protein co-localizes with cathepsin B, indicating that the enzyme probably functions in the endosomal-lysosomal compartment. This study demonstrates that the PEC genes produce functional proteases that can perform specific placental roles that are probably performed by broader specificity proteases in human placenta.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protein processing by the placental protease, cathepsin P.Mol Hum Reprod. 2009 Jul;15(7):433-42. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap029. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009. PMID: 19346238 Free PMC article.
-
Trophoblast cell differentiation: establishment, characterization, and modulation of a rat trophoblast cell line expressing members of the placental prolactin family.Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):2895-906. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-2895. Endocrinology. 1991. PMID: 1954876
-
Transplantable rat choriocarcinoma cells express placental lactogen: identification of placental lactogen-I immunoreactive protein and messenger ribonucleic acid.Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):3131-7. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-3131. Endocrinology. 1990. PMID: 2249643
-
Placental 57-kDa Ca(2+)-binding protein: regulation of expression and function in trophoblast calcium transport.Dev Biol. 1998 Jul 1;199(1):80-92. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.8926. Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9676194
-
Evolution of placentally expressed cathepsins.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Apr 26;293(1):23-9. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00167-5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 12054558
Cited by
-
Protein processing by the placental protease, cathepsin P.Mol Hum Reprod. 2009 Jul;15(7):433-42. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap029. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009. PMID: 19346238 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary n-3-PUFA supplementation, post-insemination plane of nutrition and pregnancy status on the endometrial transcriptome of beef heifers.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 27;10(1):20798. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77604-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33247230 Free PMC article.
-
Brentuximab vedotin exerts profound antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic efficacy in CD30-positive as well as cocultured CD30-negative germ cell tumour cell lines.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jan;22(1):568-575. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13344. Epub 2017 Sep 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 28941150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakanishi T, Ozaki Y, Blomgren K, Tateyama H, Sugiura-Ogasawara M, Suzumori K. Role of cathepsins and cystatins in patients with recurrent miscarriage. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2005;11:351–355. - PubMed
-
- Varanou A, Withington SL, Lakasing L, Williamson C, Burton GJ, Hemberger M. The importance of cysteine cathepsin proteases for placental development. J Mol Med. 2006;84:305–317. - PubMed
-
- Freeman SJ, Lloyd JB. Inhibition of proteolysis in rat yolk sac as a cause of teratogenesis. Effects of leupeptin in vitro and in vivo. J.Embryol.Exp.Morph. 1983;78:183–193. - PubMed
-
- Afonso S, Romagnano L, Babiarz B. The expression and function of cystatin C and cathepsin B and cathepsin L during mouse embryo implantation and placentation. Development. 1997;124:3415–3425. - PubMed
-
- Ambroso JL, Harris C. In vitro embryotoxicity of the cysteine proteinase inhibitors benzyloxycarbonyl-phenylalanine-alanine-diazomethane(Z-Phe-Ala-CHN2) and benzyloxycarbonyl-phenylalanine-phenylalanine-diazomethane (Z-Phe-Phe-CHN2) Teratology. 1994;50:214–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

