Mutations in alpha-tubulin cause abnormal neuronal migration in mice and lissencephaly in humans
- PMID: 17218254
- PMCID: PMC1885944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.017
Mutations in alpha-tubulin cause abnormal neuronal migration in mice and lissencephaly in humans
Abstract
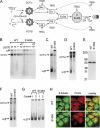
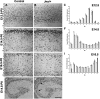
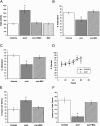
The development of the mammalian brain is dependent on extensive neuronal migration. Mutations in mice and humans that affect neuronal migration result in abnormal lamination of brain structures with associated behavioral deficits. Here, we report the identification of a hyperactive N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-induced mouse mutant with abnormalities in the laminar architecture of the hippocampus and cortex, accompanied by impaired neuronal migration. We show that the causative mutation lies in the guanosine triphosphate (GTP) binding pocket of alpha-1 tubulin (Tuba1) and affects tubulin heterodimer formation. Phenotypic similarity with existing mouse models of lissencephaly led us to screen a cohort of patients with developmental brain anomalies. We identified two patients with de novo mutations in TUBA3, the human homolog of Tuba1. This study demonstrates the utility of ENU mutagenesis in the mouse as a means to discover the basis of human neurodevelopmental disorders.
Figures




References
-
- Angevine J.B., Jr. Time of neuron origin in the hippocampal region. An autoradiographic study in the mouse. Exp. Neurol. 1965;(Suppl 2):1–70. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman D.M., Deacon R.M., Brady S., Bruce A., Sprengel R., Seeburg P.H., Rawlins J.N. A comparison of GluR-A-deficient and wild-type mice on a test battery assessing sensorimotor, affective, and cognitive behaviors. Behav. Neurosci. 2004;118:643–647. - PubMed
-
- Bartolini F., Bhamidipati A., Thomas S., Schwahn U., Lewis S.A., Cowan N.J. Functional overlap between retinitis pigmentosa 2 protein and the tubulin-specific chaperone cofactor C. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:14629–14634. - PubMed
-
- Basten C.J., Zeng Z.B., Weir B.S. Academic Press; San Diego: 1996. QTLCartographer: a suite of programs for mapping quantitative trait loci. Abstracts to Plant Genome, IV.
-
- Boycott K.M., Flavelle S., Bureau A., Glass H.C., Fujiwara T.M., Wirrell E., Davey K., Chudley A.E., Scott J.N., McLeod D.R., Parboosingh J.S. Homozygous deletion of the very low density lipoprotein receptor gene causes autosomal recessive cerebellar hypoplasia with cerebral gyral simplification. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005;77:477–483. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

