NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN
- PMID: 17218260
- PMCID: PMC1828909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.039
NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN
Abstract
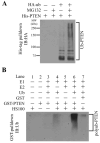
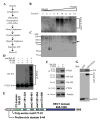
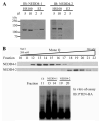
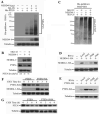
The tumor suppressor PTEN, a critical regulator for multiple cellular processes, is mutated or deleted frequently in various human cancers. Subtle reductions in PTEN expression levels have profound impacts on carcinogenesis. Here we show that PTEN level is regulated by ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation, and purified its ubiquitin ligase as HECT-domain protein NEDD4-1. In cells NEDD4-1 negatively regulates PTEN stability by catalyzing PTEN polyubiquitination. Consistent with the tumor-suppressive role of PTEN, overexpression of NEDD4-1 potentiated cellular transformation. Strikingly, in a mouse cancer model and multiple human cancer samples where the genetic background of PTEN was normal but its protein levels were low, NEDD4-1 was highly expressed, suggesting that aberrant upregulation of NEDD4-1 can posttranslationally suppress PTEN in cancers. Elimination of NEDD4-1 expression inhibited xenotransplanted tumor growth in a PTEN-dependent manner. Therefore, NEDD4-1 is a potential proto-oncogene that negatively regulates PTEN via ubiquitination, a paradigm analogous to that of Mdm2 and p53.
Figures
Comment in
-
PTEN enters the nuclear age.Cell. 2007 Jan 12;128(1):25-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.023. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17218252 Review.
References
-
- Adey NB, Huang L, Ormonde PA, Baumgard ML, Pero R, Byreddy DV, Tavtigian SV, Bartel PL. Threonine phosphorylation of the MMAC1/PTEN PDZ binding domain both inhibits and stimulates PDZ binding. Cancer Res. 2000;60:35–37. - PubMed
-
- Bakkers J, Camacho-Carvajal M, Nowak M, Kramer C, Danger B, Hammerschmidt M. Destabilization of DeltaNp63alpha by Nedd4-mediated ubiquitination and Ubc9-mediated sumoylation, and its implications on dorsoventral patterning of the zebrafish embryo. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:790–800. - PubMed
-
- Blot V, Perugi F, Gay B, Prevost MC, Briant L, Tangy F, Abriel H, Staub O, Dokhelar MC, Pique C. Nedd4.1-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent recruitment of Tsg101 ensure HTLV-1 Gag trafficking towards the multivesicular body pathway prior to virus budding. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2357–2367. - PubMed
-
- Bond GL, Hu W, Levine AJ. MDM2 is a central node in the p53 pathway: 12 years and counting. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005;5:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Brooks CL, Gu W. Ubiquitination, phosphorylation and acetylation: the molecular basis for p53 regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:164–171. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

