Parallel SUMOylation-dependent pathways mediate gene- and signal-specific transrepression by LXRs and PPARgamma
- PMID: 17218271
- PMCID: PMC1850387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.11.022
Parallel SUMOylation-dependent pathways mediate gene- and signal-specific transrepression by LXRs and PPARgamma
Abstract
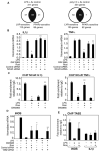
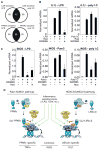
Transrepression is widely utilized to negatively regulate gene expression, but the mechanisms by which different nuclear receptors effect gene- and signal-specific transrepression programs remain poorly understood. Here, we report the identification of alternative SUMOylation-dependent mechanisms that enable PPARgamma and LXRs to negatively regulate overlapping but distinct subsets of proinflammatory genes. Ligand-dependent conjugation of SUMO2/3 to LXRs or SUMO1 to PPARgamma targets them to promoters of TLR target genes, where they prevent the signal-dependent removal of NCoR corepressor complexes required for transcriptional activation. SUMO1-PPARgamma and SUMO2/3-LXRs inhibit distinct NCoR clearance mechanisms, allowing promoter- and TLR-specific patterns of repression. Mutational analysis and studies of naturally occurring oxysterol ligands indicate that the transactivation and SUMOylation-dependent transrepression activities of LXRs can be independently regulated. These studies define parallel but functionally distinct pathways that are utilized by PPARgamma and LXRs to differentially regulate complex programs of gene expression that control immunity and homeostasis.
Figures





Comment in
-
Wrestling rules in transrepression: as easy as SUMO-1, -2, -3?Mol Cell. 2007 Jan 26;25(2):178-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.009. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17244526 Review.
References
-
- Baek SH, Ohgi KA, Rose DW, Koo EH, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. Cell. 2002;110:55–67. - PubMed
-
- Castrillo A, Joseph SB, Vaidya SA, Haberland M, Fogelman AM, Cheng G, Tontonoz P. Crosstalk between LXR and toll-like receptor signaling mediates bacterial and viral antagonism of cholesterol metabolism. Mol Cell. 2003;12:805–816. - PubMed
-
- Chiang JY, Kimmel R, Stroup D. Regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) transcription by the liver orphan receptor (LXRalpha) Gene. 2001;262:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Costet P, Luo Y, Wang N, Tall AR. Sterol-dependent transactivation of the ABC1 promoter by the liver X Receptor/Retinoid X receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:28240–28245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

