L13a blocks 48S assembly: role of a general initiation factor in mRNA-specific translational control
- PMID: 17218275
- PMCID: PMC1810376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.11.028
L13a blocks 48S assembly: role of a general initiation factor in mRNA-specific translational control
Abstract
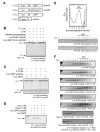
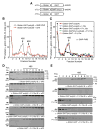
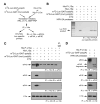
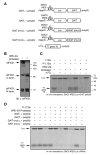
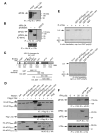
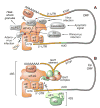
Transcript-specific translational control restricts macrophage inflammatory gene expression. The proinflammatory cytokine interferon-gamma induces phosphorylation of ribosomal protein L13a and translocation from the 60S ribosomal subunit to the interferon-gamma-activated inhibitor of translation (GAIT) complex. This complex binds the 3'UTR of ceruloplasmin mRNA and blocks its translation. Here, we elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying repression by L13a. Translation of the GAIT element-containing reporter mRNA is sensitive to L13a-mediated silencing when driven by internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) that require initiation factor eIF4G, but is resistant to silencing when driven by eIF4F-independent IRESs, demonstrating a critical role for eIF4G. Interaction of L13a with eIF4G blocks 43S recruitment without suppressing eIF4F complex formation. eIF4G attack, e.g., by virus, stress, or caspases, is a well-known mechanism of global inhibition of protein synthesis. However, our studies reveal a unique mechanism in which targeting of eIF4G by mRNA-bound L13a elicits transcript-specific translational repression.
Figures

References
-
- Anthony DD, Merrick WC. Analysis of 40 S and 80 S complexes with mRNA as measured by sucrose density gradients and primer extension inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:1554–1562. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann K, Grskovic M, Gebauer F, Hentze MW. A dual inhibitory mechanism restricts msl-2 mRNA translation for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Cell. 2005;122:529–540. - PubMed
-
- Cho PF, Poulin F, Cho-Park YA, Cho-Park IB, Chicoine JD, Lasko P, Sonenberg N. A new paradigm for translational control: inhibition via 5′-3′ mRNA tethering by Bicoid and the eIF4E cognate 4EHP. Cell. 2005;121:411–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

