What is heterogeneity and is it important?
- PMID: 17218716
- PMCID: PMC1767262
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39057.406644.68
What is heterogeneity and is it important?
Abstract
This is the first in a series of occasional articles explaining statistical and epidemiological tests used in research papers in the BMJ
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

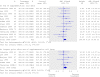
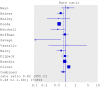
References
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Summarising effects across studies. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions 4.2.6 [updated Sep 2006]; Section 8.6. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4. Chichester: Wiley, 2006. www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
