Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP300
- PMID: 17220215
- PMCID: PMC2597984
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2006.046698
Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP300
Abstract
Background: Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) is a congenital disorder characterised by growth retardation, facial dysmorphisms, skeletal abnormalities and mental retardation. Broad thumbs and halluces are the hallmarks of the syndrome. RSTS is associated with chromosomal rearrangements and mutations in the CREB-binding protein gene (CREBBP), also termed CBP, encoding the CREB-binding protein. Recently, it was shown that mutations in EP300, coding for the p300 protein, also cause RSTS. CBP and EP300 are highly homologous genes, which play important roles as global transcriptional coactivators.
Objective: To report the phenotype of the presently known patients with RSTS (n = 4) carrying germline mutations of EP300.
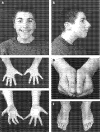
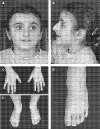
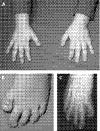
Results: The patients with EP300 mutations displayed the typical facial gestalt and malformation pattern compatible with the diagnosis of RSTS. However, three patients exhibited much milder skeletal findings on the hands and feet than typically observed in patients with RSTS.
Conclusions: Part of the clinical variability in RSTS is explained by genetic heterogeneity. The diagnosis of RSTS must be expanded to include patients without broad thumbs or halluces.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
-
- Hennekam R C. Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 200614981–985. - PubMed
-
- Stevens C A, Hennekam R C, Blackburn B L. Growth in the Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet Suppl 1990651–55. - PubMed
-
- Rubinstein J H, Taybi H. Broad thumbs and toes and facial abnormalities. A possible mental retardation syndrome. Am J Dis Child 1963105588–608. - PubMed
-
- Petrij F, Giles R H, Dauwerse H G, Saris J J, Hennekam R C, Masuno M, Tommerup N, van Ommen G J, Goodman R H, Peters D J, Breuning M H. Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome caused by mutations in the transcriptional co‐activator CBP. Nature 1995376348–351. - PubMed
-
- Roelfsema J H, White S J, Ariyurek Y, Bartholdi D, Niedrist D, Papadia F, Bacino C A, den Dunnen J T, van Ommen G J, Breuning M H, Hennekam R C, Peters D J. Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome: mutations in both the CBP and EP300 genes cause disease. Am J Hum Genet 200576572–580. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous