Detection of human CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2J2 in cardiovascular tissues
- PMID: 17220242
- PMCID: PMC2747652
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.106.012823
Detection of human CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2J2 in cardiovascular tissues
Abstract
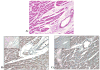
The cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2J2 metabolize arachidonic acid to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, which are known to be vital in regulation of vascular tone and cardiovascular homeostasis. Because there is limited information regarding the relative expression of these P450 enzymes in cardiovascular tissues, this study examined the expression of CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2J2 mRNA and protein in human heart, aorta, and coronary artery samples by real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, and immunohistochemistry. CYP2J2 and CYP2C9 mRNA levels were highly variable in human hearts, whereas CYP2C8 mRNA was present in lower abundance. CYP2J2 mRNA was approximately 10(3) times higher than CYP2C9 or CYP2C8 in human heart. However, CYP2C9 mRNA was more abundant than CYP2J2 or CYP2C8 in one ischemic heart. In human aorta, mean CYP2C9 mRNA levels were approximately 50 times higher than that of CYP2J2 and 5-fold higher than that of CYP2C8. In human coronary artery, mean values for CYP2C9 mRNA were approximately 2-fold higher than that of CYP2J2 mRNA and 6-fold higher than that of CYP2C8 mRNA. Immunoblotting results show relatively high levels of CYP2J2 and CYP2C8 protein in human hearts, which was confirmed by immunohistochemistry. CYP2C9 protein was also detected at high levels in one ischemic heart by immunoblotting. CYP2C9 was present at higher levels than CYPJ2 in aorta and coronary artery, whereas CYP2C8 protein was below the limits of detection. The expression of CYP2J2 and CYP2C8 in human heart, and CYPC9 and CYP2J2 in aorta and coronary artery is consistent with a physiological role for these enzymes in these tissues.
Figures





References
-
- Busse R, Fleming I. Regulation of endothelium-derived vasoactive autacoid production by hemodynamic forces. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Campbell WB, Gebremedhin D, Pratt PF, Harder DR. Identification of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors. Circ Res. 1996;78:415–423. - PubMed
-
- Campbell WB, Harder DR. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors and vascular cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in the regulation of tone. Circ Res. 1999;84:484–488. - PubMed
-
- Capdevila JH, Falck JR, Harris RC. Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid bioactivation. Molecular and functional properties of the arachidonate monooxygenase. J Lipid Res. 2000;41:163–181. - PubMed
-
- Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998;91:3527–3561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

